J Comput Assist Tomogr 2000 Mar-Apr;24(2):274-80
Comparison of FDG-PET with MIBI-SPECT in the detection of breast cancer
and axillary lymph node metastasis.
Yutani K, Shiba E, Kusuoka H, Tatsumi M, Uehara T, Taguchi T, Takai SI, Nishimura T.
Department of Radiology, Kaizuka City Hospital, Osaka, Japan.
[email protected]
PURPOSE: The purpose of this work was to compare [18F]2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-glucose (FDG) PET
and 99mTc-methoxyisobutylisonitrile (MIBI) SPECT in the detection of breast cancer and
axillary lymph node metastasis in the same patients. METHOD: FDG-PET and MIBI-SPECT were
performed within 3 days for 40 women (age range 25-86 years old) with suspected breast
cancer, in whom biopsies and/or mastectomies were performed. Both images were visually
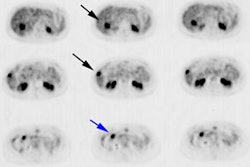
assessed, and the count ratio between tumor and normal tissue (T/N ratio) was calculated.
RESULTS: Thirty-eight patients had breast cancer, and the remaining two had benign breast
lesions. The sensitivities of FDG-PET and MIBI-SPECT were 78.9 and 76.3% for breast cancer
and 50.0 and 37.5% for axillary lymph node metastasis, respectively. The T/N ratio of
breast cancer was significantly higher in FDG-PET (6.01 +/- 3.08 mean +/- SD) than that in
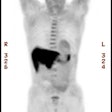
MIBI-SPECT (3.48 +/- 1.21) (p = 0.01). Nonmalignant diffuse uptake of FDG in the breasts
and the accumulation of MIBI in heart and liver occasionally obscured tumor uptake.
CONCLUSION: These results indicate that MIBI-SPECT is comparable with FDG-PET in detecting
breast cancer. Neither FDG-PET nor MIBI-SPECT is sufficiently sensitive to rule out
axillary lymph node metastasis.