Sunday, November 27 | 10:30 a.m.-11:30 a.m. | S2-SSPH02-4 | Room N229
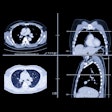
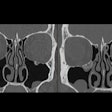
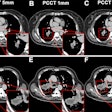
Dual-energy conebeam CT (DECT) yields higher brain image quality than single-energy conebeam CT in patients presenting with ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, a Swedish researcher will report during this Sunday session.The use of conebeam CT for interventional procedures and diagnostic workup has been on the rise, presenter Dr. Fredrik Stahl of Karolinska Institute in Solna, Sweden, and colleagues noted in their study abstract. Single-energy conebeam CT is effective, but the team sought to explore whether using dual-layer conebeam CT would further reduce artifacts and better visualize brain structures.
Stahl's group conducted a study that included 28 stroke patients who underwent conventional CT on presentation at the hospital and then a dual-energy cone-beam exam the day after admission; these were matched with 30 matched image sets. The researchers compared structure visualization, gray- and white-matter differentiation, and the presence of artifacts on a five-point scale.
Dual-energy conebeam CT performed better on all measures, Stahl and colleagues found, leading them to conclude that "[dual-energy] detector cone-beam CT may improve intracranial image quality over standard [single-energy] conebeam CT."
Attend this scientific presentation to learn more.