CT can help clinicians differentiate accidental head trauma from trauma caused by abuse in infants, researchers have reported.
The findings could improve care of this vulnerable population, as "differentiating accidental head trauma and abusive head trauma (AHT) may be challenging in infants," wrote a team led by Valeria Della Valle, MD, of Armand Trousseau Hospital in Paris, France. The results were published on August 4 in Pediatric Radiology.
Della Valle and colleagues conducted a study that assessed CT exams in 306 infants presenting with apparent accidental low-velocity trauma, tracking any features considered to be indicative of abusive head trauma, such as rupture of bridging veins. They used data from 306 children (mean age, 5 months) who had experienced any kind of minor head trauma between 2014 and 2022 that led to an emergency visit and had available clinical and head CT scan information. Examples of causes of head trauma included a fall from a height of 6 feet or less, a direct head impact, or a low-velocity road accident (below 9 miles per hour).
Of the study cohort, 89 (29%) had fractures. Of these, 71 (80%) were simple linear fractures.
The team reported the following:
- 34 patients had intracranial hemorrhage.
- 26 patients had simple post-traumatic focal extra-axial hemorrhage.
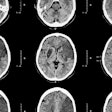
- Eight patients had more complex hemorrhage on CT and MRI. Of these, three showed bridging vein rupture, a finding associated with abusive head trauma.
Of the three infants who showed bridging vein rupture, a child protection team "expressed concern that two might have experienced abusive head trauma, while the third patient had a condylar fracture, and it remains unclear whether the injury was the result of abusive head trauma or an accidental fall," Della Valle and colleagues wrote.
The study results could help differentiate between accidental and abusive head trauma in infants, according to the researchers.
"The main CT scan features following minor accidental trauma in infants are simple skull fractures and scalp swelling," they concluded. "Diffuse hemorrhage with rupture of bridging veins is exceptional in this context."
The complete study can be found here.







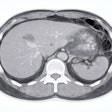
![Images show the pectoralis muscles of a healthy male individual who never smoked (age, 66 years; height, 178 cm; body mass index [BMI, calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared], 28.4; number of cigarette pack-years, 0; forced expiratory volume in 1 second [FEV1], 97.6% predicted; FEV1: forced vital capacity [FVC] ratio, 0.71; pectoralis muscle area [PMA], 59.4 cm2; pectoralis muscle volume [PMV], 764 cm3) and a male individual with a smoking history and chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) (age, 66 years; height, 178 cm; BMI, 27.5; number of cigarette pack-years, 43.2, FEV1, 48% predicted; FEV1:FVC, 0.56; PMA, 35 cm2; PMV, 480.8 cm3) from the Canadian Cohort Obstructive Lung Disease (i.e., CanCOLD) study. The CT image is shown in the axial plane. The PMV is automatically extracted using the developed deep learning model and overlayed onto the lungs for visual clarity.](https://img.auntminnie.com/mindful/smg/workspaces/default/uploads/2026/03/genkin.25LqljVF0y.jpg?auto=format%2Ccompress&crop=focalpoint&fit=crop&h=112&q=70&w=112)