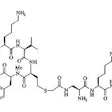
CEA-Scan ? ? (arcitumomab)
Imaging Protocol
PATIENT PREPARATION
? Have the patient drink plenty of fluids on the day prior to the study
? Have the patient drink normal amounts of fluid several hours before injection
? Inject the patient with 25 - 30 mCi Tc-99m CEA-Scan intravenously (a butterfly is suggested to ensure a good injection)
? Have the patient void just prior to imaging; catheterize the bladder if activity may obscure pelvic disease.
IMAGING PROTOCOL
? Begin imaging at 2.5 hours post injection.
? Use a large field of view (LFOV) camera with a low-energy high-resolution collimator (LEHR). Energy setting should have a 20% window width centered at 140 keV Tc-99m peak.
? Images should be acquired in the following order.
1) SPECT IMAGING OF PELVIS: Use a 128 X 128 X 16 matrix for best results.
Images should be acquired using step and shoot technique with 3-degree stops for multi-head camera and 6-degree stops for single-head systems. Acquire each projection for 30 to 40 seconds per stop.
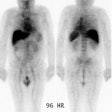
2) PLANAR WHOLE BODY IMAGING: Acquire anterior and posterior whole body scan at a speed of 8 - 10cm / minute or spot view images for 10 minutes per view.
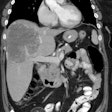
3) SPECT IMAGING OF ABDOMEN: Acquired in the same manner as the SPECT of pelvis above. Liver should be centered in the FOV.
4) DELAY SPECT IMAGING AT 8 – 24 hrs. (if needed, however, delayed imaging 18 to 24 hours following injection has not been shown to enhance lesion detection, and may result in an increased number of false-positive exams): Use a 64 X 64 X 16 matrix. Regardless of single or multi-head system, one should use a step and shoot technique with 6-degree stops. Acquire each projection for 60 to 70 seconds per stop.
SPECT PROCESSING
? Use a filtered backprojection algorithm and reconstruct all three planes.
? Use a Butterworth or low pass filter with the order set between 6 and 10, with a cutoff frequency of 0.26 - 0.45. The cutoff frequency may be higher with a 64 X 64 matrix.
? Apply attenuation correction to abdominal reconstructed images.
? Volume-rendered 3-D or reprojected images are very useful in study interpretation.
SCAN INTERPRETATION
? CEA-Scan studies MUST be read from the computer monitor.
? Planar and SPECT images should be displayed at high intensity. Varying the intensity may enhance areas of subtle tumor uptake.
? A low intensity is necessary to properly view the liver and the tissues near hot structures such as the kidneys and bladder.
? The reader should sweep through the image planes, stopping to compare suspicious areas on all three planes. Use of a triangulation program can facilitate disease detection.