(Ultrasound Review) Occult fractures of the waist of the scaphoid can reliably be detected using high-resolution ultrasound, according to radiologists in Bordeaux, France. Scaphoid fractures have high rates of complication including "nonunion, delayed union, osteonecrosis, and secondary osteoarthritis," wrote investigators in the American Journal of Roentgenology. Early, accurate detection of scaphoid fractures reduces the "rate of complications and the risk of secondary displacement."
Also, an early negative result means normal wrists are not unnecessarily immobilized. "The rate of negative findings on initial conventional radiographs is high, ranging from 20% to 25%," they reported.
In a prospective study of 54 consecutive patients, those with a clinically suspected fracture and negative radiography were scanned with high-frequency ultrasound to assess the scaphoid bone and surrounding soft tissues. Presenting symptoms included "pain, tenderness on axial loading of the first ray, and swelling at the level of the anatomic snuff-box." Injury was due to a fall on an outstretched hand or direct trauma. The waist of the scaphoid is the most common site for a fracture to occur (70%), the authors reported.
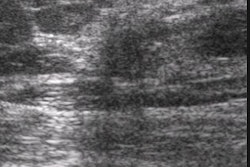
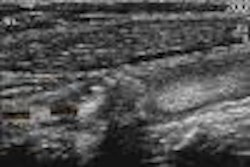
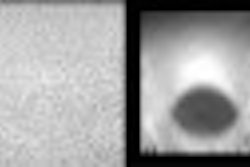
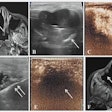
Using ulnar deviation to elongate the scaphoid, images were obtained in longitudinal and transverse with a 12 MHz linear array transducer. "Attention was paid to the continuity of the anterior echogenic margin of the scaphoid corresponding to the cortex and the surrounding soft tissues. Scaphoid fracture was considered if the cortex was discontinuous," they said. The soft tissues surrounding the scaphoid were examined for hemarthrosis (diffuse, compressible collection) and hematoma (focal, incompressible collection).
The best ultrasound criterion for diagnosis was cortical disruption. This resulted in a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 98%. There was one false negative result in an elderly patient with arthritis who had irregularity of the cortex of the tubercle. There were 16 patients with either hematoma or hemarthrosis and no cortical disruption, and none had a scaphoid fracture using additional imaging modalities including CT, MRI and bone scan.
The authors concluded "early evaluation of the scaphoid bone after wrist trauma is important to initiate prompt treatment in cases of occult fracture, because early treatment substantially decreases the rate of complication and avoids overtreatment of patients without fracture."
"Occult fractures of the waist of the scaphoid -- early diagnosis by high-spatial-resolution sonography"O Hauger et al
Service de radiologie, Groupe Hospitallier Pellegrin, Bordeaux Cedex, France
AJR; 2002 April; 178:1239-1245
By Ultrasound Review
June 26, 2002
Copyright © 2002 AuntMinnie.com