Dear Advanced Visualization Insider,
Virtual reality (VR) technology has many applications in radiology, including for surgical planning and education. But it can also be quite helpful for patients.
This issue's Insider Exclusive details how VR can make the placement of peripheral intravenous catheters less painful and anxiety-inducing for pediatric patients. In a randomized clinical trial, patients who were able to play a VR game during the procedure had significantly lower anxiety and pain scores after catheter placement than those who just received the standard of care.
In a similar vein, researchers from King's College London found that VR could help patients decrease their anxiety and claustrophobia during MRI scans. It may also be useful for research in areas such as functional MRI.
Meanwhile, an automated MR image segmentation algorithm can enable the use of augmented reality (AR) by neurosurgeons, according to a Dutch group. The algorithm generates 3D models that neurosurgeons can utilize for AR-based viewing and surgical planning.
Radiomics continues to demonstrate predictive power across a variety of clinical applications. A CT radiomics model was reported to be valuable for predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with advanced gastric cancer. In addition, radiomics analysis of F-18 FDG-PET exams aided in predicting relapse in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Also, radiomics analysis can stratify risk in low-dose CT lung screening exams.
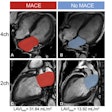
A new study has shown that sarcopenia can be measured on both chest and abdominal CT examinations by a deep-learning algorithm. The ability to measure this important risk factor for future hip fractures and death at the L1 vertebrae on CT could greatly expand the potential yield of opportunistic CT screening, according to the researchers.
In addition, body composition analysis was able to foretell outcomes in COVID-19 patients. Two specific measures were associated with admission to the intensive care unit as well as death, according to the authors. Also, a 3D liver segmentation method can rapidly diagnose and measure liver fat on cardiac CT exams.
Artificial intelligence (AI) tools bundled with advanced visualization platforms have traditionally accounted for most of the medical imaging AI market. But will that dominance continue in the future? Sanjay Parekh, PhD, of Signify Research shared his thoughts on the matter in a recent column.
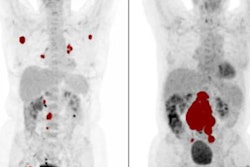
Researchers from Spain have also concluded that 3D SPECT exams and an AI algorithm can assist physicians in determining a patient's stage of Parkinson's disease, potentially enabling physicians to adjust treatment based on disease severity.
Is there a story you'd like to see covered in the Advanced Visualization Community? Please feel free to drop me a line.