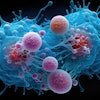
| FIGURE 1.1.7 Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). Contrast-enhanced CT images (A and B) show multiple polypoid soft tissue lesions within the contrast-filled colon, including a dominant polypoid mass (asterisk) in the ascending colon. Images from subsequent colonoscopy (C and D) again demonstrate the multiple adenomatous polyps and the larger mass, which proved to be a tubulovillous adenoma with multiple foci of adenocarcinoma. Note the "cerebriform" appearance to the overlying mucosa often seen with adenomatous neoplasia. Double-contrast BE images (E and F) from two different patients with FAP show innumerable sessile filling defects representing adenomas. (A to D from Pickhardt PJ: Differential diagnosis of polypoid lesions seen at CT colonography (virtual colonoscopy). Radiographics 2004; 24:1535-1559.) |
Atlas of Gastrointestinal Imaging Figure 1.1.7 Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
Latest in Home
Using GPT‑4o with CT exams helps diagnose ovarian cancer earlier
February 18, 2026
Survey: Nearly 4 out of 5 practices short on breast imagers
February 18, 2026
Cardiac MRI-based ML model predicts MACE risk for STEMI patients
February 17, 2026