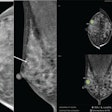
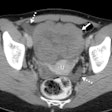
| FIGURE 1.1.5 Villous adenomas 3D endoluminal CTC (A) image shows a large, lobulated cecal mass. On prone 2D transverse CTC (B), the mass is submerged under the opacified fluid, which outlines its frond-like nature. The villous appearance is confirmed at colonoscopy (C). 3D endoluminal CTC image (D) from a second patient shows a relatively flat lobulated rectal mass (arrowheads), which carpets the mucosal surface. Note the rectal catheter (arrow. Images from subsequent colonoscopy (E) and EUS (F) show the same 5-cm mass. There is no evidence of submucosal extension at EUS, and this lesion proved to be a benign villous adenoma with high-grade dysplasia. 3D endoluminal CTC (G), 2D sagittal CTC (H), and colonoscopy (I) images from a third patient show another rectal villous adenoma manifesting as a flat carpet lesion, which involves a relatively large surface area and extends near the anorectal junction. |
Atlas of Gastrointestinal Imaging Figure 1.1.5 Villous adenomas
Latest in Home
New benchmark helps monitor cumulative CT radiation dose
February 13, 2026
Study questions routine use of radiotherapy after bone surgery
February 13, 2026