PET imaging with an experimental radiotracer appears better than standard SPECT imaging with iodine-123 metaiodobenzylguanidine (I-123 MIBG) in patients with neuroblastoma, according to a study published September 4 in the Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
The tracer -- an analog of MIBG labeled with F-18 -- requires less scan time and detects more lesions, noted lead author Neeta Pandit-Taskar, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and colleagues.
“F-18 MFBG-PET imaging provides efficient single-day high-resolution imaging of neuroblastoma, with superior lesion detection and Curie scores compared with I-123 MIBG imaging and has the potential to improve treatment management for these patients,” the group wrote.
Neuroblastoma is a type of pediatric cancer that develops in immature nerve tissue (neuroblasts). I-123 MIBG-SPECT is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for imaging neuroblastoma and is well integrated into clinical routine, yet it requires a two-day protocol and administration of iodine to prevent radiation damage to the thyroid from I-123, the researchers explained.
Previously, the group created metafluorobenzylguanidine (MFBG), an analog of MIBG that can be labeled with F-18 for PET imaging, and tested it successfully for the first time in humans in 2018. In this study, they expanded their research in a detailed comparison between F-18 MFBG and I-123 MIBG imaging in 37 patients.
The cohort included patients ages 4 to 45 with relapsed or refractory neuroblastoma. Patients were given F-18 MFBG intravenously, followed by imaging 60 minutes after injection. All study participants also had an I-123 MFBG-SPECT/CT scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis within four weeks. All detected lesions were noted for each modality.
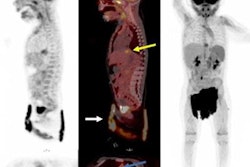
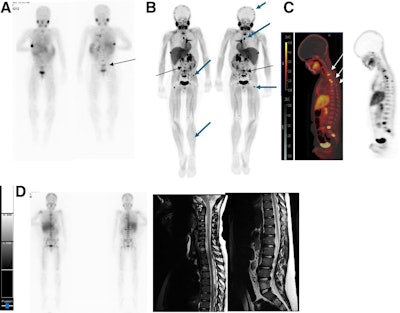 I-123 MIBG–negative and F-18 MFBG–positive scans showing multiple lesions in 9-year-old male with relapsed high-risk, multiple-relapse neuroblastoma (stage IV disease) receiving chemoimmunotherapy. (A) I-123 MIBG uptake is seen in lower lumbar vertebrae (arrows). Positive uptake with F-18 MFBG PET (B; black arrows) in skull, spine, pelvic bones, femora, and left tibia (B and C; blue and white arrows). Bone marrow biopsy was positive for disease. Follow-up I-123 MIBG imaging (D; left) and spine MRI (D; right) performed six weeks later showed diffuse disease in skull and spine, corresponding to F-18 MFBG–avid sites. Journal of Nuclear Medicine
I-123 MIBG–negative and F-18 MFBG–positive scans showing multiple lesions in 9-year-old male with relapsed high-risk, multiple-relapse neuroblastoma (stage IV disease) receiving chemoimmunotherapy. (A) I-123 MIBG uptake is seen in lower lumbar vertebrae (arrows). Positive uptake with F-18 MFBG PET (B; black arrows) in skull, spine, pelvic bones, femora, and left tibia (B and C; blue and white arrows). Bone marrow biopsy was positive for disease. Follow-up I-123 MIBG imaging (D; left) and spine MRI (D; right) performed six weeks later showed diffuse disease in skull and spine, corresponding to F-18 MFBG–avid sites. Journal of Nuclear Medicine
Overall, more lesions were noted on the F-18 MFBG scans (mean, 18; range, 0-61) compared with the I-123 MIBG scans (mean, 12; range, 0-44), and 455 lesions were concordant. Finally, the Curie score (a measure of tracer uptake) for F-18 MFBG was higher, with an average of 11 (range, 0-25) compared with 8 for I-123 MIBG (range, 0-22), the group reported.
“F-18 MFBG-PET offers faster imaging and superior detection compared with I-123 MIBG imaging,” the researchers wrote.
Additional studies that examine the role of F-18 MFBG versus I-123 MIBG for treatment response assessment will be critical for determining its predictive and prognostic value, the group concluded.
The full study is available here.