Imaging plays a key role in diagnosing renovascular disease and in determining the future course of treatment. Imaging modalities play a specific role in finding evidence for renin mediation and in showing stenosis of the main renal artery, its major branches, or accessory arteries. When renal artery stenosis (RAS) is suspected, the imaging strategy can include a variety of modalities, such as Doppler ultrasound, CT angiography, ACE-inhibition scintigraphy, and digital subtraction angiography (DSA).
At the recently concluded 6th Asia-Pacific Congress of Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiology in Delhi, Dr Srikanth Moorthy, a consultant with the department of radiology at Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences and Research Centre (AIMS) in Cochin, suggested a diagnostic algorithm when RAS is suspected based on clinical symptoms. Screening is recommended in patients showing one or more clinical symptoms.
RAS should be suspected with cases of abrupt onset of hypertension before 30 years of age (indicative of dysplasia), abrupt onset at or later than 50 years (indicative of atherosclerosis), accelerated or malignant hypertension, or refractory hypertension unresponsive to three or more drugs. Renal abnormalities such as unexplained azotemia, azotemia following ACE inhibitor use, unilateral small kidney, and unexplained hypokalemia are also cause for suspicion.
Other findings may include abnormal bruit; carotid, coronary, and peripheral vascular disease; and additionally, unexplained congestive cardiac failure and pulmonary edema.
Ultrasound
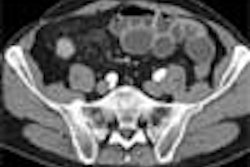
In Moorthy's algorithm, the first step is to screen suspected RAS cases using Doppler ultrasound to look for the following indicators: renal artery stenosis, renal size, evidence of parenchymal damage, mass, and polycystic disease. The drawback with this modality is that the main renal artery is not clearly visualised in as high as 40% of individuals, although intraparenchymal segmental and arcuate arteries can be consistently imaged, Moorthy said.
Quoting from a paper published in Clinical Nephrology, Moorthy said that when arteries are adequately visualised, peak systolic velocity greater than 180-200 cm/sec or a reno-aortic peak systolic velocity ratio greater than 3.5 are considered as reliable criteria to detect significant stenosis. Stenosis in accessory renal arteries may also go undetected. A combined approach of interrogating the main and intrarenal branches has a sensitivity of 96% and a specificity of 98% for detecting RAS compared to angiography (May 2000, Vol. 53:5, pp. 333-343).
Patients with poor outcomes after revascularisation can be identified by ultrasound. For poor outcomes, a renal resistive index of more than 0.8 is taken as the marker.
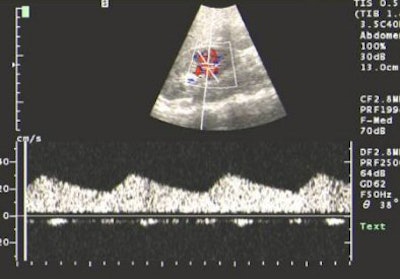
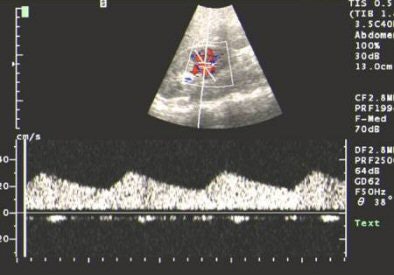 |
| US showing tardus-parvus pattern in the arcuate artery. All images courtesy of Dr Srikanth Moorthy, Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences and Research Centre, Cochin. |
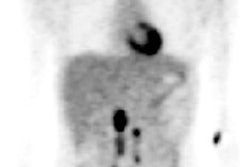
ACE-inhibition scintigraphy
This technique has a sensitivity of 80% and a specificity of 100%. It can also quantify renal function, so a nonfunctional kidney can be managed by nephrectomy, which shows better results, rather than revascularisation.
DSA intervention is recommended when the outcome is a high probability scan, as indicated by a distinctive change in the renal curve, unilateral decreased tracer uptake, and unilateral increased transit time. An intermediate probability report calls for further noninvasive imaging studies to confirm RAS.
An intermediate probability report may be required when there is an abnormal renal curve because of baseline renal impairment that makes interpretation of the post-ACE-inhibitor scan difficult, Moorthy said.
MR/CT angiography
CT angiography (CTA) is ideal for imaging accessory renal arteries. And CTA with spiral and multidetector-row scanners provides better resolution compared to MR angiography (MRA). Maximum intensity projections (MIP) and volume-rendering algorithms can also be used to analyse the dataset (Radiology, May 1999, Vol. 211:2, pp. 337-343). CTA is also very useful in providing a road map for surgery because the 3D relationship of the vessels in the renal hilum can be visualised.
However, with CTA there is risk of contract-induced nephrotoxicity in patients with baseline renal impairment or diabetes. Taking this into consideration along with the risk from radiation, MRA may be a better choice for RAS. "MRA is emerging as the most important noninvasive imaging modality for stenosis," Moorthy said.
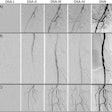
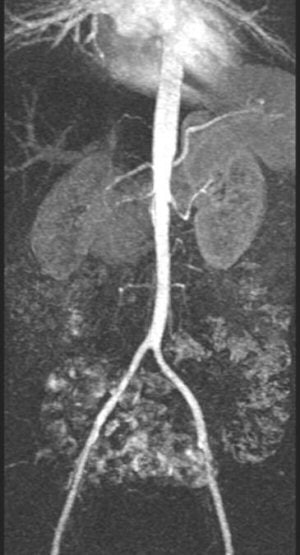 |
| Contrast-enhanced MRA showing long-segment stenosis of the right renal artery. |
3D spoiled gradient-echo, gadolinium-enhanced breath-hold imaging is required for adequate visualisation of the renal artery. MRA studies for RAS have shown good results, with 97% sensitivity and 92% specificity for stenosis grading and detecting peripheral stenosis and accessory arteries (Radiology, February 2001, Vol. 218:2, pp. 481-490).
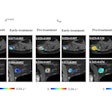
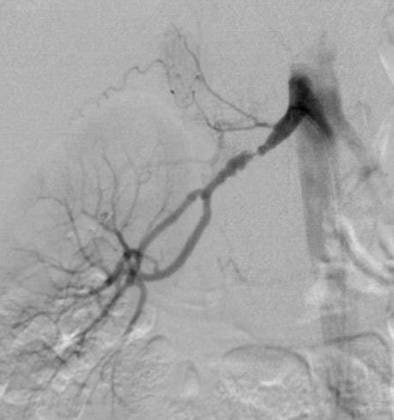 |
| DSA in the same patient showing periadventitial-type fibromuscular dysplasia. |
"DSA is the gold standard for detection of RAS, but invasive catheter angiography is best reserved for therapeutic intervention," Moorthy said. He recommended MRA as the first imaging modality of choice if cost was not a constraint, but that DSA should be used as the first diagnostic test only in cases with a high index of suspicion.
By N. Shivapriya
AuntMinnieIndia.com staff writer
November 18, 2004
Copyright © 2004 AuntMinnie.com