Graphics processing unit technology developer Nvidia is introducing a new healthcare artificial intelligence (AI) computing platform, as well as a new relationship with MD Anderson Cancer Center, at this week's GPU Technology Conference (GTC) Fall 2021.
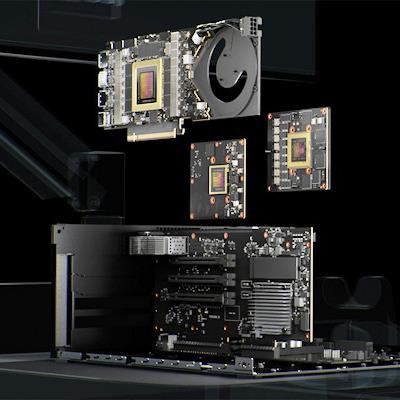
Clara Holoscan is designed to provide the computational infrastructure to enable medical device developers to build applications that process multimodality sensor data, run physics-based models, accelerate AI inferencing, and render high-quality graphics in real-time, according to the vendor. It provides scalable, end-to-end processing of streaming data for medical devices.
"Holoscan seamlessly bridges medical devices with edge servers in the hospital and allows developers to create AI microservices to run low-latency streaming applications on devices while passing more complex tasks on to the hospital data center," said Kimberly Powell, vice president of healthcare at Nvidia.
By using Nvidia's Fleet Command cloud service with Holoscan, devices can also be remotely managed, orchestrated, and updated, Powell added.
"That's truly going to enable the software-as-a-service model for medical devices," she said.
Meanwhile, the Clara Holoscan SDK, which will be available on November 15, features acceleration libraries, AI models, and reference applications in ultrasound, digital pathology, endoscopy, and more, according to the vendor.
 Nvidia's Clara Holoscan is an AI development platform for software-defined medical devices. Image courtesy of Nvidia.
Nvidia's Clara Holoscan is an AI development platform for software-defined medical devices. Image courtesy of Nvidia.In other news, Nvidia is now also partnering with MD Anderson Cancer Center on cancer-focused AI initiatives. The institution is implementing a data-driven approach to cancer, combining continuous capture of healthcare data with Nvidia's DGX systems and development of new AI models in a range of new applications, according to the company.
Several radiology AI initiatives are underway, including new AI models aimed at early detection of pancreatic cancer -- a leading cause of cancer deaths that's often identified only after it has metastasized.
"We're working on AI models to analyze the pancreas anytime we see it in a CT scan, MRI study or endoscopic ultrasound, whether or not the patient's appointment is related to the pancreas," said Dr. Eugene Koay, PhD, co-director of gastrointestinal radiation oncology at MD Anderson, in a statement from Nvidia.
Koay and his group are also collaborating with the Early Detection Research Network to develop convolutional neural networks that can spot the cases that are most likely to progress into malignant cancer, Nvidia said.
Other AI initiatives underway at MD Anderson include image-contouring models for planning of radiotherapy treatments and MRI-assisted radiosurgery, as well an algorithm that analyzes post-treatment prostate MRI studies to assess the quality of radiation delivery.
In addition, the institution is working on an anomaly detection project to identify the cases that cause CT liver tumor contouring models to fail. With this understanding, the researchers can add additional training examples to more efficiently improve performance, according to Nvidia.
"We don't want to keep collecting data that looks the same as our first 150 scans," said Kristy Brock, PhD, a professor of imaging physics and radiation physics, in a Nvidia statement. "We want to identify cases that will increase the variability of our sample dataset, which in turn boosts the model's accuracy and generalizability."