Reperfusion edema after thromboendarterectomy: radiographic patterns of disease.
Miller WT Jr, Osiason AW, Langlotz CP, Palevsky HI
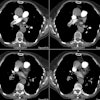
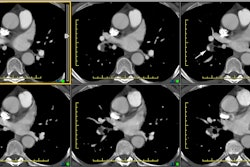
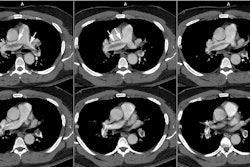
In patients with chronic pulmonary embolism, pulmonary thromboendarterectomy may result in a unique form of noncardiogenic pulmonary edema termed reperfusion edema. This report reviews the authors' experience after pulmonary thromboendarterectomy with particular emphasis on the radiographic manifestations of reperfusion edema. The clinical and radiographic record of 25 patients who underwent pulmonary thromboendarterectomy at the University of Pennsylvania from 1985 through 1995 were reviewed. The zonal distribution of radiographic opacity, time to maximal opacity, and the time to clearance of reperfusion edema were determined. The relationship of these radiographic manifestations to clinical severity of disease and clinical outcome was examined. Reperfusion edema, characterized by patchy bilateral perihilar alveolar opacities, occurred in all but one patient. There is a lower lung zone predominance of opacities, but in individual cases, striking unilateral or haphazard arrangements of opacities may be seen. In this small sample of patients, no association between preoperative pulmonary arterial pressures and radiographic appearance or clinical outcome was found. However, severity of radiographic opacities, as measured by the extent of involved lung, correlated with disease severity, as measured by time to extubation and time to discharge. Pneumonia, defined as a radiographic opacity that evolves discordantly with the reperfusion edema opacities, occurred in 20% of cases. Reperfusion edema is a common consequence of pulmonary thromboendarterectomy. The severity of radiographic manifestations and clinical severity of disease are related. This characteristically appears as perihilar alveolar opacities.