Minnies finalists, page 3
Best Radiology Image
First x-ray image taken in space. Image from Chun Wang, et al.
The first finalist for Best Radiology Image is out of this world -- literally, it is the first x-ray taken in space.
The image was acquired during the Fram2 space mission led by 42-year-old cryptocurrency entrepreneur Chun Wang. The mission launched on March 31 from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. On April 1, the all-civilian crew woke up, had breakfast, and “took a few x-ray images,” Wang wrote in a post on the social media platform X.
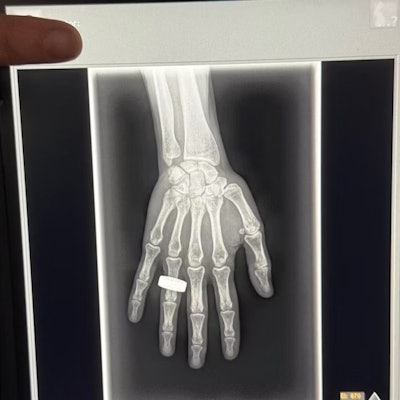 Image from an X post by @satofishi.
Image from an X post by @satofishi.
Sharp observers will note that the image bears a resemblance to the first x-ray ever taken by Wilhelm Roentgen of his wife Anna Bertha Ludwig's hand on December 22, 1895.
That was intentional.
“The crew members were informed of Wilhelm Roentgen’s first x-ray image and were excited to honor that pioneering achievement 129 years later by recreating the image in space,” said Jeanne Walter, vice president of marketing and sales for MinXray, the company that manufactured the portable x-ray machine used to acquire the image.
An analysis of the acquired data and images is still underway, and findings will be shared once the research is complete, Walter added.
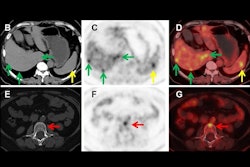
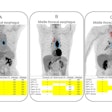
PET scans identify people at early risk for cognitive decline. Image from Guilherme Kolinger, MD, of Life Molecular Imaging in Germany, et al.
The second finalist for Best Radiology Image comes from a study reporting that amyloid PET scans in individuals with early signs of Alzheimer’s disease can identify those at higher risk of cognitive decline.
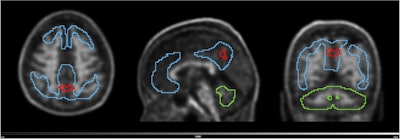 Image available for republishing under Creative Commons license (CC BY 4.0 DEED, Attribution 4.0 International) and courtesy of the European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Image available for republishing under Creative Commons license (CC BY 4.0 DEED, Attribution 4.0 International) and courtesy of the European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
The study was conducted by scientists at Lantheus subsidiary Life Molecular Imaging, with the image demonstrating how quantitative analysis can reveal additional insights beyond standard visual assessment in amyloid PET.
“To identify the region highlighted in red, an amyloid-negative population (at baseline) with subjective cognitive decline was assessed with a voxel-based analysis using standardized uptake value ratios (SUVRs). Then, the baseline SUVR images of amyloid accumulators versus nonaccumulators were compared. Amyloid accumulation status was defined using the Centiloid method and with a five-year follow-up,” lead author Guilherme Kolinger, MD, explained to AuntMinnie.
The results showed that accumulators exhibited higher baseline SUVR in the red-marked region, which corresponds to part of the precuneus, a brain area known to play a role in early Alzheimer's disease. This region overlaps with the Centiloid target region (shown in blue), underscoring the potential of this approach to enhance preclinical Alzheimer's disease assessment, Kolinger added.
Scientific Paper of the Year
Private Equity Acquisitions of Radiology Practices from 2013 to 2023: National- and State-Level Analyses. Khunte, et al, American Journal of Roentgenology, March 5, 2025. To learn more about this paper, click here.
First up in the finalists that the Minnies expert panel picked for Scientific Paper of the Year is a study that found that private equity firms acquired more than 150 radiology practices involving nearly 3,500 locations between 2013 and 2023.
Mihir Khunte and Yashaswini Singh, PhD, from Brown University in Providence, RI, were motivated by the rapid rise of private equity investment in healthcare in the U.S., in particular in physician practices, and a relative gap in rigorous data on how these trends affect radiology.
Compared with 2013, when 0.88% of all radiologists in the study were under private equity employment, the research duo reported that 11.7% of all radiologists nationally in 2023 were private equity-employed. The latter includes 12% of all diagnostic radiologists and 6.7% of all interventional radiologists who were under this employment.
“Private equity acquisitions may introduce efficiencies and capital improvements but also raise concerns regarding physician autonomy, higher cost of care, and shifts in clinical priorities with unclear benefit for patients,” Singh told AuntMinnie.
Projected Lifetime Cancer Risks From Current Computed Tomography Imaging. Smith-Bindman, et al, JAMA Internal Medicine, April 14, 2025. To learn more about this paper, click here.
The second finalist for Scientific Paper of the Year presented findings suggesting that cancers associated with radiation from CT scans could eventually account for 5% of all new cases annually. The fallout of the findings is included in the Minnies Most Significant News Event in Radiology category this year.
Led by Rebecca Smith-Bindman, MD, a group at the University of California, San Francisco developed a risk model based on approximately 93 million scans in 62 million patients in 2023.
The team found that approximately 103,000 radiation-induced cancers were projected to result from 93 million scans. Risks were higher in children and adolescents, yet higher CT use in adults accounted for most (93,000) radiation-induced cancers, the researchers reported.
“I would love to see radiology professional organizations step up and acknowledge the overuse [of CT scans], acknowledge the low-value imaging and try to come up with some strategies for how we can address this,” Smith-Bindman told AuntMinnie in a recent interview.
Best New Radiology Device
Magnetom Flow.Ace, Siemens Healthineers
The Magnetom Flow.Ace is an ultrapremium, wide-bore, 1.5 tesla high-performance gradient MRI system cleared for use in the U.S. in June.
 The Magnetom Flow.Ace 1.5-tesla MRI scanner.Siemens Healthineers
The Magnetom Flow.Ace 1.5-tesla MRI scanner.Siemens Healthineers
The scanner is the company's first 1.5-tesla platform for MR imaging with a closed helium circuit and no quench pipe. The system has a 60 cm bore and is also the first Siemens MRI scanner to be marketed to the veterinary radiology community as well as for general radiology, with coils now available for both fields.
“The Flow.Ace is a combination of all the best that’s come before it. The lack of helium is what’s most exciting for us,” said Katie Grant, PhD, head of Magnetic Resonance at Siemens Healthineers North America.
The Magnetom Flow.Ace requires just 0.7 liters of liquid helium for cooling, compared with conventional MRI scanners, which require more than 1,000 liters. This feature is due to the magnet’s DryCool technology, the company said.
The system design also eliminates the need for a quench pipe. In conventional scanners, this is needed to safely allow large amounts of gaseous helium to escape directly into the atmosphere during an emergency shutdown. The company also highlighted that the Magnetom Flow.Ace reduces annual energy consumption by more than 30%, owing to the system's Eco Power Mode.
The Magnetom Flow.Ace was 17 years in the making, Grant noted.
Signa Sprint, GE HealthCare
First debuted at the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine in May, the Signa Sprint is an ultrapremium, wide-bore, 1.5-tesla high-performance gradient MRI system.
 The Signa Sprint 1.5-tesla MRI scanner.GE HealthCare
The Signa Sprint 1.5-tesla MRI scanner.GE HealthCare
With a high-gradient performance of 65/200 per axis driving the system, the system is designed to deliver crystal-clear visualization of submillimetric structures, improved signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) on diffusion imaging, and includes deep-learning algorithms to support diagnostics and treatment response monitoring, the company noted.
“This new system supports clinicians’ shift to quantitative MRI and a deeper understanding of tissue characteristics,” said Fotis Vlachos, chief strategy, marketing, and commercial officer, MR, at GE HealthCare.
Signa Sprint features built-in AI technologies AIR Recon DL, Sonic DL, and AIR x, according to GEHC. The system aims to enable accelerated cardiac MRI through the use of deep-learning reconstruction techniques to help reduce the time and expertise needed to interpret scans and drive consistency and reliability.
As breakthrough cancer therapies get introduced and cardiac MRI becomes increasingly adopted in clinical routine, the demand for higher precision and speed in diffusion and functional imaging is driving MR beyond its current standard of care, according to the company.
The mission of Signa Sprint is to offer capabilities once available only with high-end 3-tesla MRI systems in a field strength that is considered standard for oncological and cardiological MR imaging, Vlachos noted.
Best New Radiology Software
Protect Her AI women’s health software platform, Covera Health
Our first finalist for Best New Radiology Software is an AI-powered women’s health software platform designed to identify early signs of breast cancer, cardiovascular disease, and osteoporosis on routine scans.
Making use of AI, Protect Her analyzes imaging studies that women are already undergoing, such as mammograms, chest CT exams, and x-rays. It then flags imaging signs and patterns that may otherwise be missed, according to Covera Health.
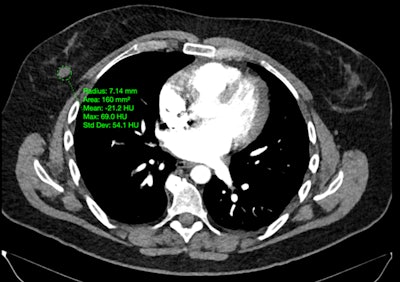 Protect Her utilizes AI-based analysis of routine imaging scans to detect early signs of breast cancer, cardiovascular disease, and osteoporosis.
Protect Her utilizes AI-based analysis of routine imaging scans to detect early signs of breast cancer, cardiovascular disease, and osteoporosis.
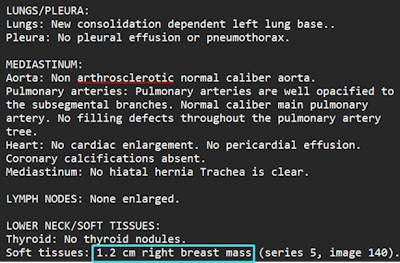
For example, Protect Her can detect patterns on mammograms that can indicate early malignancies, the company said. What’s more, it can spot breast arterial calcifications on mammograms and coronary artery calcium (both markers of heart disease) on chest CT exams. It can also note signs of vertebral fractures, which are often missed in early stages and can indicate osteoporosis, according to the vendor.
"Protect Her is purposefully built around women’s imaging, supporting radiologists and their primary care partners in identifying and treating early signs of breast cancer, bone disease, and cardiovascular disease,” said Gerard Heath, MD, senior vice president and chief of staff at Covera Health.
Viz 3D CTA AI software, Viz.ai
Introduced in April, our other Best New Radiology Software contender is a neurovascular imaging application that automatically converts CT angiography (CTA) scans into high-resolution AI-enhanced 3D images.
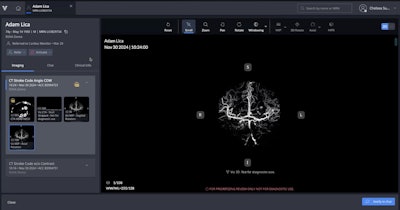 Viz 3D CTA automatically converts CT angiography scans into high-resolution AI-enhanced 3D images.Viz.ai
Viz 3D CTA automatically converts CT angiography scans into high-resolution AI-enhanced 3D images.Viz.ai
The company said that Viz 3D CTA addresses challenges in neurovascular imaging, including delays due to manual 3D renderings, limited spatial context in PACS, and difficulty viewing smaller or more distal vessel abnormalities. The software also features automated postprocessing, skull-stripped views, and interactive tools such as sagittal and axial rotation, according to Viz.ai.
“Fully integrated into the Viz.ai platform, this capability enables care teams to interact with complex neurovascular anatomy in real-time -- automatically removing bone and venous structures to enhance clarity and support time savings in stroke and aneurysm workflows," said Chelsea Summerour, associate director for product management.
Best New Radiology Vendor
Onc.ai
Onc.AI is a Series-A funded company that's developing imaging AI models for predicting clinical outcomes in cancer patients, initially focusing on metastatic lung cancer.
The firm sells models directly to pharmaceutical companies such as Pfizer, GSK, and Amgen to inform drug development. It is also developing clinical models intended for medical oncology decision support.
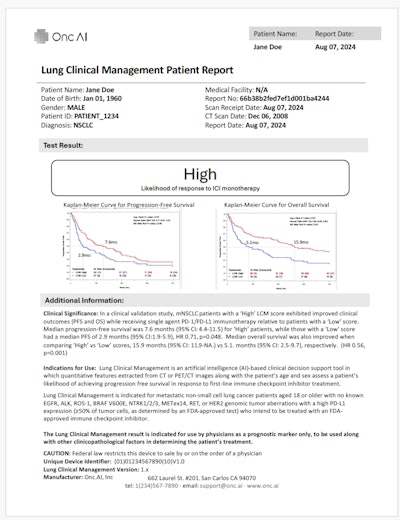 AI predictions for treatment response in metastatic lung cancer patients are provided in a PDF format.Onc.ai
AI predictions for treatment response in metastatic lung cancer patients are provided in a PDF format.Onc.ai
“Although our AI models are solely based on a cancer patient’s CT or PET/CT scan, our main user is the medical oncologist,” said Akshay Nanduri, founder and CEO.
In January, Onc.ai received a breakthrough device designation from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for its Onclara model for metastatic lung cancer; the software was previously known as Serial CT Response Score. The company hopes its first models will be cleared for marketing authorization as software-as-a-medical device (SaMD) decision-support software in the second half of 2026.
Rhapsody
The other finalist for Best New Radiology Vendor is a healthcare IT interoperability firm that unveiled its Image Director image orchestration software in August.
Designed to help healthcare organizations modernize imaging workflows and reduce infrastructure complexity, Image Director manages DICOM, HL7, and FHIR data across cloud, edge, and hybrid environments, enabling more efficient routing of imaging data between modalities, PACS, VNAs, AI models, and clinical systems, according to the vendor.
Rhapsody said that Image Director also supports efforts to consolidate multiple imaging tools, improve access to prior studies, and connect imaging data with broader clinical information to prepare health systems for multimodal AI.
Best Educational Mobile App
MRI Made Easy... well almost, BestApps (iOS)
The winner of the 2024 Minnies award for Best Educational Mobile App returns again as a finalist. MRI Made Easy continues to serve as a “classic introduction to MR physics, reimagined for iOS.”
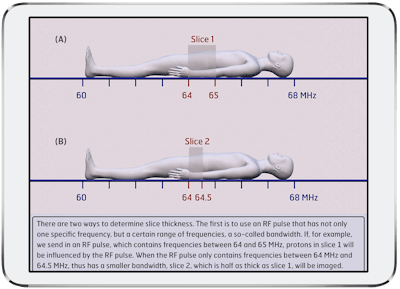 MRI Made Easy... well almost is an animated app designed to serve as an introduction to MR physics.Wouter Veldhuis, MD, PhD.
MRI Made Easy... well almost is an animated app designed to serve as an introduction to MR physics.Wouter Veldhuis, MD, PhD.
The fully animated app features a searchable, “dynamic” index designed to serve as a reference for quickly looking up MR phenomena and underlying physics. It can also be read cover to cover, according to Wouter Veldhuis, MD, PhD, of the University Medical Center Utrecht in the Netherlands.
In addition, there’s also a quiz for users on their physics knowledge. All questions are answered directly and with links to the full-text background information.
MRI Made Easy is part of the doRadiology family of educational mobile apps, which also includes perennial Minnies contender Radiology Assistant 2.0.
CTisus iQuiz 25, Elliot Fishman, MD, (iOS)
 The popular radiology quiz app is in the hunt for its second Minnie for Best Educational Mobile App.Elliot Fishman, MD.
The popular radiology quiz app is in the hunt for its second Minnie for Best Educational Mobile App.Elliot Fishman, MD.
Our second finalist is also a familiar one. The winner of the Minnies award for Best Educational Mobile App in 2020 under its previous name CTisus iQuiz, CTisus iQuiz 25 was renamed to highlight the many recent updates and upgrades to the radiology quiz app, according to Elliot Fishman, MD, of Johns Hopkins University.
“We spent so much time developing new content and improving the site, I thought an update of the name would be good,” Fishman told AuntMinnie.
The app currently provides over 1,800 magnificent cases in 15 anatomical regions. Quiz cases feature audio discussions and imaging pearls.
In the five years since iQuiz 25 won its Minnies award, the app has been upgraded to a universal app for both iPhone and iPad. Over 300 new cases have been added, and the user interface has been improved to deliver a smoother and more pleasant experience for the users, Fishman said.
Continue reading: Back to Page 1, Back to Page 2.