Radiology 1997 Jan;202(1):105-110
Small pulmonary lesions detected at CT: clinical importance.
Munden RF, Pugatch RD, Liptay MJ, Sugarbaker DJ, Le LU
Department of Radiology, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, Mass, USA.
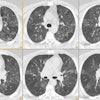
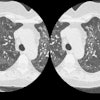
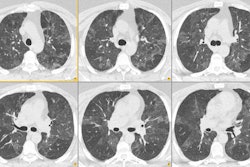
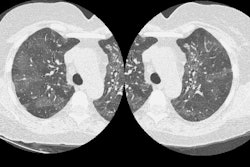
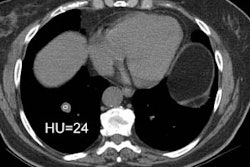
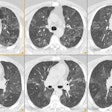
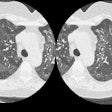
PURPOSE: To evaluate the histopathologic findings of pulmonary nodules 1 cm or smaller detected at computed tomography (CT) that were removed at video-assisted thorascopic surgery. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Clinical, radiologic, and histopathologic findings were retrospectively reviewed in 64 patients (48 women, 16 men; aged 22-85 years) who underwent video-assisted thorascopic surgical resection of small pulmonary lesions present on CT scans.
RESULTS:
Sixty-four patients had a total of 65 lesions resected. Of the 64 patients, 37 (58%) patients had no known previous malignancy and 27 (42%) had previous malignancy. Overall, 58% (38 of 65 [95% confidence interval = 0.45, 0.73]) of these lesions were malignant. Among the patients without previous malignancy, 14 (38%) had lung carcinoma (10 [27%], primary bronchogenic carcinoma; four [11%], carcinoid). In patients with a previous malignancy, malignant lesions were diagnosed in 81% (22 of 27). This included seven (26%) patients with bronchogenic carcinoma as a second primary carcinoma. In patients without previous malignancy, benign lesions were diagnosed in 59% (22 of 37); in patients with previous malignancy, benign lesions were diagnosed in 18% (five of 27). CONCLUSION: A considerable number of the malignant lesions were primary bronchogenic carcinoma. In addition, diagnosis in patients with a previous malignancy other than suspected metastatic disease can substantially alter treatment. For these reasons, early biopsy with an acceptable technique for diagnosis of these lesions is recommended.
PMID: 8988198, MUID: 97141948