Radiology 2000 Jul;216(1):93-6
Autologous blood clot seal to prevent pneumothorax at CT-guided lung biopsy.
Lang EK, Ghavami R, Schreiner VC, Archibald S, Ramirez J.
PURPOSE: To determine whether the use of autologous blood clot seal (ABCS) after
biopsy of lung lesions can reduce or prevent pneumothorax. MATERIALS AND
METHODS: The authors evaluated 100 patients (63 men, 37 women; age range, 27-78
years) with pleural (n = 23) or deep (n = 77) lesions. Thirty-eight patients had
emphysema. Patients were randomly assigned to one of two groups: those in whom
the biopsy track was sealed with autologous blood clot (n = 50) and those who
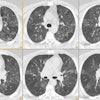
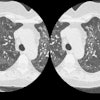
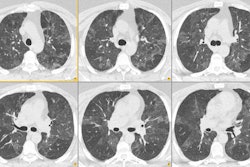
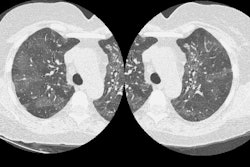
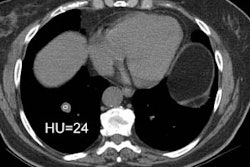
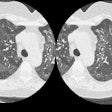
did not receive autologous blood clot (n = 50). Biopsy was performed with
computed tomographic (CT) guidance and a 19-gauge coaxial system. The autologous
blood clot, which ranged from 0.5 to 4.5 mL, was injected while the sheath was
being withdrawn. RESULTS: Pneumothorax developed in four of the 23 patients
(17%) with pleural lesions and 19 of the 77 patients (24%) with deep lesions.
Pneumothorax occurred in four of the 45 patients (9%) who had deep lesions and
received autologous blood clot and in 15 of the 32 patients (47%) who had deep
lesions and did not receive autologous blood clot (P <.001). In patients with
emphysema, pneumothorax occurred in three of the 20 patients (15%) who received
autologous blood clot and 10 of the 14 (71%) who did not (P <.001). There
were seven large pneumothoraces necessitating treatment; all occurred in
patients who did not receive autologous blood clot. CONCLUSION: Plugging of
biopsy tracks with ABCS, particularly after biopsy of deep lung lesions,
significantly reduced the frequency of pneumothorax-particularly of large
pneumothoraces-and, therefore, the need for treatment and the attendant cost.