J Thorac Imaging 1995;10(2):129-133
HRCT evaluation of secondary lobules and acini of the lung.
Giovagnorio F, Cavallo V
Dipartimento di Medicina Sperimentale, Universita, La Sapienza,
Rome, Italy.
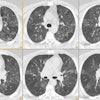
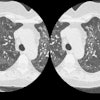
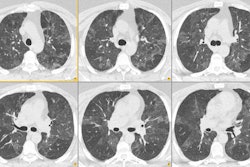
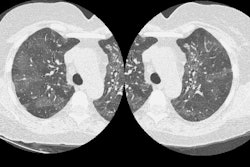
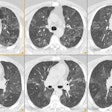
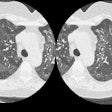
We evaluated normal lung parenchyma with high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) to assess the visibility of lobular and sublobular structures. Series of HRCT slices were obtained using the usual parameters for HRCT examinations. We used a limited reconstruction field (4-10 cm) with a narrow window to increase visibility of small structures. The boundaries of normal secondary lobules are difficult to identify because the septa are very thin; interstitial disease may increase septal thickness so that more lobules become visible. Position and approximate morphology of lobules can be identified, however, by observing the centrolobular bundles. Normally, many acini are usually visible; their mean diameter (6 mm) and thickness of periacinar capillary net (approximately 0.3 mm) make them identifiable with modern CT scanners. In conclusion, a good knowledge of HRCT lung anatomy is essential to correctly evaluate early interstitial disease.
PMID: 7769628, MUID: 95287416