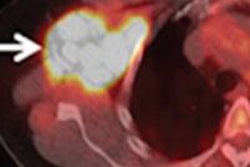
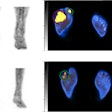
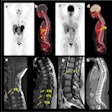
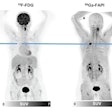
"We have developed an automated analytical technique of hot spots using SPECT/CT images," study co-author Atsushi Teramoto, PhD, from Fujita Health University in Japan, told AuntMinnie.com. "This method calculates the volume of hot spots in SPECT images inside the bone region obtained by CT images."
Commercial software that analyzes uptake regions in bone scintigraphy has recently become available, according to the researchers. But there are limitations: for example, the technique can't resolve overlaps because it relies on 2D images. However, the new technique analyzes SPECT/CT images, making it possible to analyze uptake regions in 3D while tying the results to accurate anatomical information from CT.
After the bone regions are extracted from CT, hot spots are extracted from the SPECT image using thresholding and 3D labeling, the group wrote. Hot-spot estimation errors ran less than 2%.
The proposed method will be useful for quantitative evaluation of hot spots in whole-body SPECT/CT exams, Teramoto and colleagues concluded.