Tracheal Bronchus (Pig bronchus):
Clinical:
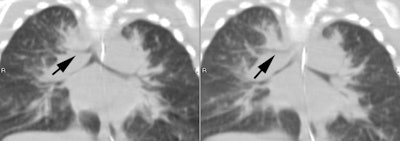
Rarely (0.1-1.3% of the population) a bronchus arises directly from the trachea prior to the carina (usually within 2 cm) - most commonly to the apical segment to the right upper lobe. This is also referred to as a "pig" bronchus. Associated conditions have been reported in 78% of children with a right tracheal bronchus including Down syndrome, thoracic cage/foregut/lung malformations, tracheal stenosis, and other tracheobronchial branching abnormalities [3]. The condition may be associated with recurrent pneumonia, stridor, or respiratory distress in children [3]. Adults are almost invariably asymptomatic [3].
|
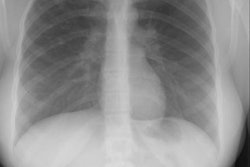
Pig bronchus (black arrow): Neonate with persistent intermittent RUL atelectasis |
|
|
Accessory cardiac bronchus: A cardiac bronchus typically arises
from the medial aspect of the bronchus intermedius, or less
commonly, from the right mainstem bronchus, and extends in an
inferior direction toward the pericardium [2]. It is usually
asymptomatic [2].
REFERENCES:
(1) Radiographics 2002; Zylak CF. Developmental lung anomalies in
the adult: radiologic-pathologic correlation. 22: S25-S43
(2) AJR 2015; Heidinger BH, et al. Imaging of large airways
disorders. 205: 41-56
(3) Radiographics 2016; Chassagnon G,et al. Tracheobronchial
branching abnormalities: lobe-based classification scheme. 36:
358-373