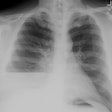
Diffuse Pleural Fibrosis:
Clinical:
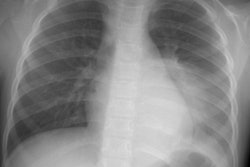
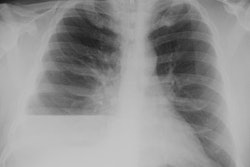
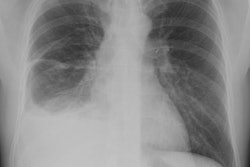
Diffuse pleural fibrosis may be the sequela of: an organized hemorrhagic effusion, tuberculus effusion (associated with extensive calcification), empyema, or asbestos related pleurisy (affects visceral pleura and is much less common than pleural plaques).X-ray:
Diffuse pleural thickening produces smooth pleural density (which can be over 1 cm in thickness) extending over at least one-fourth of the lenght of the chest wall, with or without costophrenic angle obliteration. On CT the disorder characteristically spares the mediastinal pleura (which is often involved by mesothelioma). On CT, the lesion should be at least 8 cm in length, 3 mm thick, and 5 cm broad. Calcification may occur.REFERENCES:
(1) ACR Syllabus #40: p.495-97