Technologists play a vital role in the reduction of radiation dose and image noise during CT scanning. One of the most effective techniques for reducing dose is patient positioning.
Automatic tube current modulation (ATCM) is one of the most important improvements in the history of computed tomography. Since the concept was introduced by Haaga et al1 in 1981 and made commercially available by GE Medical Systems (now GE Healthcare) in 1994,2 ATCM has become one of the principal techniques for the optimization of patient radiation dose and image quality.
In order to use ATCM, the scanner must estimate the attenuation characteristics of the patient over the range of the scan provided by one or two localizer radiographs (LRs, or topograms).3 ATCM then automatically adjusts the tube current according to the patient size and attenuation to maintain the noise level indicated by the user.
The bowtie filter was introduced to compensate for the variation of patient attenuation at the level of the detector during scan rotation.4 The filter is composed of a thinner and thicker segment. The thinner segment allows maximum beam intensity for anatomical regions with high attenuation while the thicker segment is used to reduce beam intensity for anatomical regions with lower attenuation, in the peripheral areas of the patient.5 A Teflon bowtie filter is shown in Figure 1.
 Figure1. A Teflon bowtie filter. Reproduced from M.A. Habibzadeh et al.6
Figure1. A Teflon bowtie filter. Reproduced from M.A. Habibzadeh et al.6In order to ensure that ATCM and bowtie filter techniques work as intended, the patient must be correctly centered with respect to the CT gantry. Proper centering will lead to accurate localizer radiographs and therefore optimal ATCM performance (Fig. 2a).
If the patient is positioned too close to the x-ray source, the scanner will overestimate the patient size and thus the patient attenuation (Fig. 2b). This will cause the ATCM system to transmit a higher tube current, causing an unnecessary increase in dose. If the patient is positioned too far from the x-ray source, the opposite will happen: an underestimation of the patient size and attenuation, leading to potentially noisy images (Fig. 2c).5
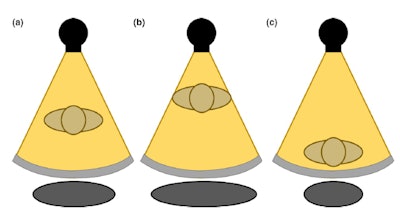 Figure 2. The gray circle at the bottom represents patient size when (a) the patient is centered at the gantry (b) an anterior shift is present in patient positioning (c) a posterior shift is present in patient positioning. Reproduced from Barreto et al.5
Figure 2. The gray circle at the bottom represents patient size when (a) the patient is centered at the gantry (b) an anterior shift is present in patient positioning (c) a posterior shift is present in patient positioning. Reproduced from Barreto et al.5The correct function of the bowtie filter also relies on centering, and the assumption that the thickest region of the patient is positioned in the center of the beam (Fig. 3). If the patient is not centered with respect to the gantry, dose will be higher than necessary in some regions of the patient, and lower than necessary in other regions.
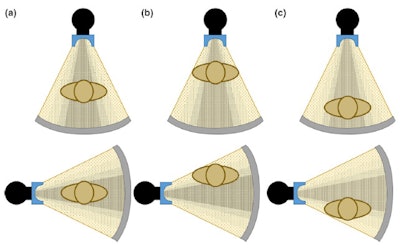 Figure 3. Anterior (top) and lateral (bottom) positions of the x-ray tube when the patient is (a) in the center of the gantry (b) shifted anteriorly (c) shifted posteriorly with respect to the beam output. Reproduced from Barreto et al.5
Figure 3. Anterior (top) and lateral (bottom) positions of the x-ray tube when the patient is (a) in the center of the gantry (b) shifted anteriorly (c) shifted posteriorly with respect to the beam output. Reproduced from Barreto et al.5This can cause nonuniform noise in the image following reconstruction. Moreover, possible shading artifacts may occur due to beam hardening from changes in the mean beam energy that can lead to artifactual changes in organ density (Fig. 4).7
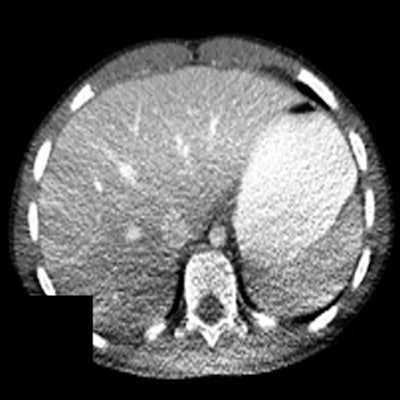 Figure 4. Shading artifacts as a result of beam hardening can be seen on the CT scan in the posterior region of the patient, causing an artifactual change in liver density. Reproduced from Szczykutowicz et al.7
Figure 4. Shading artifacts as a result of beam hardening can be seen on the CT scan in the posterior region of the patient, causing an artifactual change in liver density. Reproduced from Szczykutowicz et al.7Vertical and lateral shifts: quantified
Vertical miscentering has been reported for 73%5 to 95%8 of patients in various hospitals.9,10 Maximum reported vertical miscenterings were 6.6 cm and 3.4 cm below and above the isocenter, respectively,10 with mean shifts in the range of -2.3 cm to 2.6 cm.10,11
Miscentering was found to be more likely for smaller patients: slim adults4,6 and smaller pediatric4 patients. Moreover, many technologists often use only the anterior-posterior (AP) topogram, as opposed to both AP and lateral topograms.6 Vertical shifts of > 3 cm were found to occur in 7.7% to 22% of the cases, and such shifts are expected to be detected by technologists.5,9,10
Lateral miscentering with respect to the x-ray tube was reported for 80% of patients in one study,5 but the shift was > 0.5 mm, and supports the overall small shifts in lateral patient position across multiple studies.4,10,11 It is assumed that this is due to the fact that the borders of the patient table provide sufficient reference for the technologist.
How miscentering affects dose and image quality
Effect on dose
A magnification of 4 cm was found to increase dose by 67%, increasing CT dose index volume (CTDIvol) and size-specific dose estimate (SSDE) by 10 mGy and 11.9 mGy, respectively.12
Patient positioning of 2.5 cm to 3.5 cm below the isocenter increases dose by up to 15% in chest exams.4 Miscentering by 6 cm with respect to the bowtie filter increases surface dose by 41% to 49%,10,11 whereas a 4-cm anterior shift increases CTDIvol by 8.5% to 10%.5,14 CTDIvol in general increases linearly with horizontal anterior distance from the isocenter.5
Vertical shifts were found to impact organ dose, specifically the lung, colon, uterus, ovary, and skin by -35% to 22% in chest abdomen pelvis CT exams at a distance of up to 4 cm from the isocenter. Additional organs, such as liver, stomach, and breast had organ dose differences in the range of -13% to 15%. Organ dose also increases with vertical distance from the isocenter.5
Furthermore, to help reduce dose, the PA localizer, as opposed to an AP localizer, is recommended for chest exams.13 When lateral topogram images were used, the impact on total patient dose i.e., CTDIvol, SSDE, and DLP is lower than in the case of PA topogram images, however, the risk to certain radiation-sensitive tissues e.g., breasts and thyroid increases due to miscentering with respect to the bowtie filter.4
Effect on image quality
Miscentering of 2.1 cm below the isocenter was found to increase image noise by 6%.6 Vertical miscentering of 6 cm was reported to increase image noise by 28% to 30%.4,10
Szczykutowicz et al investigated the effect of patient positioning on CT number that is used to diagnose clinical conditions. They found that a mispositioning of 4 cm and 6 cm above the isocenter resulted in statistically significant differences in the Hounsfield unit (HU) standard deviation. A 4-cm magnification led to standard deviations of -15 ± 5 and -8 ± 2 HU for midthorax posterior and abdomen posterior, respectively. A 6-cm magnification led to standard deviations in the range of 13-20 HU for high thorax and mid thorax posterior.7
When the patient is positioned below the isocenter in supine position, noise especially increases in the posterior region due to presence of the spine and thus higher attenuation.
Vital role of technologists
Technologists play a vital role in the reduction of patient dose and image noise, as they are responsible for determining the patient positioning prior to each scan with the use of the laser lights mounted on the scanner. Multiple studies have recognized that incorrect patient positioning may outweigh the benefits of automatic exposure control.4,15,16
The following recommendations for improving patient positioning have been offered for technologists by Mayo-Smith et al,12 Kaasalainen et al,4 and Habizadeh et al:6
- The tube should be positioned at the top of the gantry, rather than at the bottom, to avoid offsets below the isocenter.12
- Both AP and lateral (LAT) topograms should be used with the lowest acceptable tube current and tube voltage settings.6,12
- Topograms should be repeated if the patient positioning is modified, to ensure proper ATCM operation.12
- The AP topogram is more robust than the LAT, and should be performed last, since only the last topogram may be used for tube current modulation in some scanners.12
- Special attention should be paid when positioning pediatric patients, due to their smaller size and organs, and pediatric weight-based protocols should be used to determine optimal settings.4
Ultimately, of course, it is successful teamwork between technologists, radiologists, and medical physicists that allows good image quality and dose reduction in the medical imaging department.
It is difficult or even impossible to retrospectively assess exactly how the patient was positioned by the technologist. In our experience, the best assessment is performed by a dose management system.
References
- Haaga JR, Miraldi F, MacIntyre W, LiPuma JP, Bryan PJ, Wiesen E. The effect of mAs variation upon computed tomography image quality as evaluated by in vivo and in vitro studies. Radiology. 1981;138(2):449-454.
- Kopka L, Funke M, Breiter N, Vosshenrich R, Grabbe E. Anatomically adapted CT tube current-dose reduction and image quality in phantom and patient studies. Radiology. 1995;197:292-292.
- Merzan D, Nowik P, Poludniowski G, Bujila R. Evaluating the impact of scan settings on automatic tube current modulation in CT using a novel phantom. Br J Radiol. 2017;90(1069):20160308.
- Kaasalainen T, Palmu K, Reijonen V, Kortesniemi M. Effect of patient centering on patient dose and image noise in chest CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014;203(1):123-130.
- Barreto I, Lamoureux R, Olguin C, Quails N, Correa N, Rill L, Arreola M. Impact of patient centering in CT on organ dose and the effect of using a positioning compensation system: Evidence from OSLD measurements in postmortem subjects. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2019;20(6):141-151.
- Habibzadeh MA, Ay MR, Asl AK, Ghadiri H, Zaidi H. Impact of miscentering on patient dose and image noise in x-ray CT imaging: phantom and clinical studies. Phys Med. 2012;28(3):191-199.
- Szczykutowicz TP, DuPlissis A, Pickhardt PJ. Variation in CT number and image noise uniformity according to patient positioning in MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017;208(5):1064-1072.
- Namasivayam S, Kalra MK, Mittal P, Small WC. Can radiation exposure associated with abdominal and/or pelvic CT be minimized with better practice. 2006. Vancouver, Canada: ARRS.
- Kim MS, Singh S, Halpern E, Saini S, Kalra MK. Relationship between patient centering, mean computed tomography numbers and noise in abdominal computed tomography: Influence of anthropomorphic parameters. World J. Radiol. 2012;4(3):102-108.
- Toth T, Ge Z, Daly MP. The influence of patient centering on CT dose and image noise. Med Phys. 2007;34(7):3093-3101.
- Li J, Udayasankar UK, Toth TL, Seamans J, Small WC, Kalra MK. Automatic patient centering for MDCT: effect on radiation dose. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;188(2):547-552.
- Mayo-Smith WW, Hara AK, Mahesh M, Sahani DV, Pavlicek W. How I do it: managing radiation dose in CT. Radiology. 2014;273(3):657-672.
- Saltybaeva N, Krauss A, Alkadhi H. Effect of localizer radiography projection on organ dose at chest CT with automatic tube current modulation. Radiology. 2017;282(3):842-849.
- Zhang D, Ayala R. Auto couch height positioning compensation-making SURE Exposure a smarter dose reduction tool. Toshiba America Medical Systems. 2014. CTWP12271US; 1-8.
- Gudjonsdottir J, Svensson JR, Campling S, Brennan PC, Jonsdottir B. Efficient use of automatic exposure control systems in computed tomography requires correct patient positioning. Acta radiologica. 2009;50(9):1035-1041.
- Matsubara K, Koshida K, Ichikawa K, Suzuki M, Takata T, Yamamoto T, Matsui O. Misoperation of CT automatic tube current modulation systems with inappropriate patient centering: phantom studies. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;192(4):862-865.
Author biographies
 Anna Romanyukha.
Anna Romanyukha.Anna Romanyukha received her doctorate degree in medical physics from the Centre of Medical Radiation Physics (UOW, Australia) and her MSc degree in health physics from Georgetown University. She worked as a postbaccalaureate and predoctoral fellow at the U.S. National Cancer Institute (NIH, Washington DC) on various projects including radiation dose estimation from diagnostic exposures. She now works in Qaelum, focusing on advanced software tools in patient radiation dose management and quality.
 Steve Nzitunga.
Steve Nzitunga.Steve Nzitunga worked five years in AZ Monica as radiographer for general radiology, CT, MRI, and conebeam CT for ankle and feet (pedCAT). He also had radiation protection responsibilities. Currently, he works in Qaelum as application specialist for all products.
 Ana Dolcet Llerena.
Ana Dolcet Llerena.Ana Dolcet Llerena is a medical physicist from Spain and member of the Spanish Society of Medical Physics. She did her residency in Granada and, after working in a radiation protection technical unit, she is now employed by Qaelum as application specialist for Iberia, focused on patient radiation dose management.
The comments and observations expressed are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the opinions of AuntMinnie.com.