Radiology 1999 May;211(2):549-53
Hypoxemia and liver cirrhosis (hepatopulmonary syndrome) in eight patients:
comparison of the central and peripheral pulmonary vasculature.
Lee KN, Lee HJ, Shin WW, Webb WR
Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Seo-Ku,
Pusan, Korea.
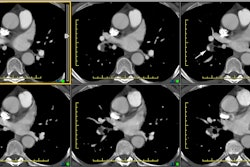
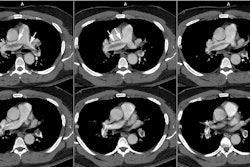
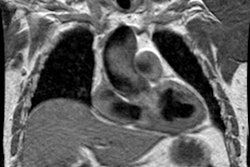
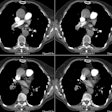
PURPOSE: To evaluate the pulmonary vasculature in patients with hepatopulmonary
syndrome. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Conventional computed tomographic (CT) scans in
eight patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome were retrospectively evaluated to
compare the diameters of the pulmonary trunk, right and left main pulmonary
arteries, and peripheral pulmonary vasculature in the right posterior basal
segment with those in eight healthy subjects and in four patients with
normoxemic cirrhosis. With thin-section CT, the ratio of segmental arterial
diameter to adjacent bronchial diameter in the right lower lobe in four patients
with hepatopulmonary syndrome was compared with that in four patients with
normoxemic cirrhosis. RESULTS: In patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome, the
peripheral pulmonary vasculature was significantly dilated compared with that in
control subjects and in patients with normoxemic cirrhosis (P = .002); however,
the central pulmonary arteries were not significantly dilated (P > .05). At
thin-section CT, the ratio of segmental arterial diameter to adjacent bronchial
diameter was significantly greater than that in patients with normoxemic
cirrhosis (P < .05). CONCLUSION: In patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome,
the peripheral pulmonary vasculature is significantly dilated. Dilatation of the
peripheral pulmonary vasculature may be helpful in the diagnosis of
hepatopulmonary syndrome.
PMID: 10228541, UI: 99245225