Congenital Critical Pulmonic Stenosis (Isolated):
Clinical:
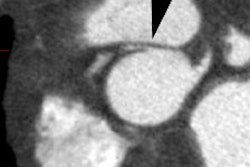
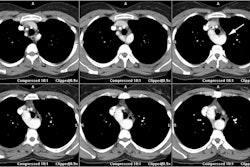
In most patients, pulmonic valvular stenosis (PVS) is an isolated anomaly that does not present until adulthood and there is generally normal pulmonary vascularity on CXR. In neonates with critical pulmonary stenosis, most or all of the blood that enters the right ventricle is returned to the right atrium due to tricuspid regurge. This reduces flow into the lungs and creates a large right-to-left shunt at the atrial level. Flow to the pulmonary circulation is dependent upon a patent ductus arteriosus. Treatment is balloon valvuloplasty.X-ray:
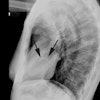
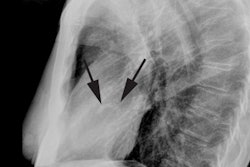
Neonates with severe pulmonic stenosis demonstrate decreased pulmonary blood flow and a bulging right heart border.REFERENCES:
(1) Pediatric Clinics of North America 1999; Waldman JD, Wernly
JA.
Cyanotic congenital heart disease with decreased pulmonary blood
flow in
children. 46(2): 385-402