Radiology 2001 Jun;219(3):629-36
Peripheral pulmonary arteries: how far in the lung does multi-detector
row spiral ct allow analysis?
Ghaye B, Szapiro D, Mastora I, Delannoy V, Duhamel A, Remy J, Remy-Jardin M.
Department of Radiology, University Center Hospital Calmette, Blvd Jules Leclerc, 59037
Lille Cedex, France (B.G., D.S., I.M., J.R., M.R.J.).
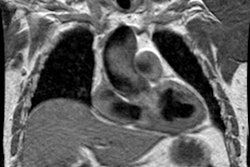
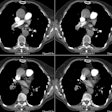
PURPOSE: To analyze the influence of multi-detector row spiral computed tomography (CT) on
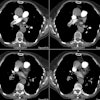
identification of peripheral pulmonary arteries. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Peripheral
pulmonary arteries were analyzed on optimally opacified contrast material-enhanced spiral
CT angiograms in 30 patients devoid of pleuroparenchymal disease who underwent scanning
with multi-detector row CT (collimation, 4 x 1 mm; pitch, 1.7-2.0; scanning time, 0.5
second). Two series of scans were systematically generated from each data set,
1.25-mm-thick (group 1) and 3-mm-thick (group 2) sections, leading to the analysis of 600
segmental (20 arteries per patient), 1,200 subsegmental (40 arteries per patient), 2,400
fifth-order (80 arteries per patient), and 4,800 sixth-order (160 arteries per patient)
pulmonary arteries in each group. RESULTS: Multi-detector row CT with reconstructed scans
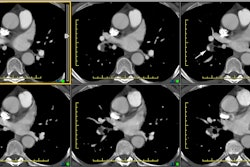
of 1.25-mm-thick sections (group 1) allowed (a) analysis of a significantly higher
percentage of subsegmental arteries (94% in group 1 vs 82% in group 2; P <.001) and (b)
a significantly higher percentage of fifth- and sixth-order arteries, respectively,
identified in 74% and 35% of cases in group 1 and 47% and 16% in group 2 (P <.001). The
causes for inadequate depiction of subsegmental branches in group 1 were partial volume
effect (43%), anatomic variants (39%), and cardiac (17%) and respiratory (1%) motion
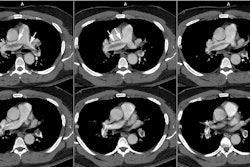
artifacts. CONCLUSION: Multi-detector row CT with reconstructed scans of 1.25-mm-thick
sections enables accurate analysis of peripheral pulmonary arteries down to the fifth
order on spiral CT angiograms.
PMID: 11376246