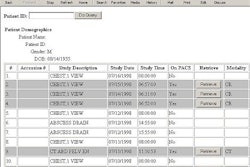
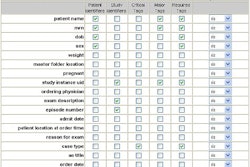
Summary of Wireless Security Standards
|
 |
| A. Bluetooth Protocol |
 |
- Uses handheld portable devices
- Designed for use within 10-meter distances
- Security operates as a "trusted device" at the data-link layer
- Device, not the user, is trusted
- Authentication is based upon a shared key
- Bluetooth is not an end-to-end security solution
|
 |
| B. Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) |
 |
- WAP specification defines protocols at the Application, Session, and Transport layers
- WAP Protocol Architecture has six layers.
- Security is provided through the Wireless Transport Layer Security (WTLS)
- WTLS provides authentication, privacy, and data integrity through the use of encryption and Message Authentication Codes (MAC)
- WAP relies on block cipher algorithms that encrypt data
|
 |
| C. Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs), IEEE 802.11 |
 |
- Security is provided through the Wired Equivalent Protocol (WEP)
- WEP uses a single shared key common to all users of a WLAN layer
- Encryption Keys can be recovered through analysis
- IEEE 802.11i (TGi) is developing the new WLAN Security
|
 |
|