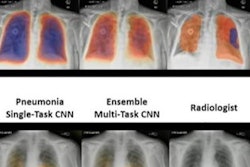
An artificial intelligence (AI) model appears effective for detecting malpositioned endotracheal tubes on patient x-rays, according to a study presented at the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) annual meeting.
A group led by researchers at Seoul National University Hospital and including colleagues at AI software firm Lunit tested a deep-learning model trained on chest x-rays from intubated patients in intensive care units. The model performed well and could potentially be used to alert clinicians of cases where tubes need to be repositioned, according to the group.
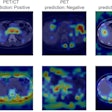
"A deep-learning system exhibited excellent performance in identifying the presence of ET [endotracheal tube] and malposition of ET on chest radiographs," noted corresponding author Dr. Eui Jin Hwang, in a thoracic imaging poster presentation.
Chest x-rays are used to evaluate tube placements after clinicians have intubated patients, as improperly positioned tubes can cause complications. Tubes inserted in patients too deeply can cause contralateral lung collapse or ipsilateral hyperinflation, while shallowly inserted tubes can result in air leaks or vocal cord injuries, the authors explained. They hypothesized that a deep-learning AI model could help evaluate tube placements and ultimately reduce morbidity rates associated with these complications.
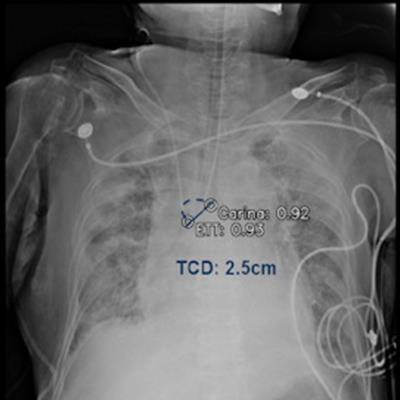
The team developed a model based on 539 consecutive portable chest x-rays taken immediately after tube insertions in patients in internal care units at their hospital. The model was trained to identify the presence versus absence of endotracheal tubes and correct placements based on distances between the tube tip and the ridge at the end of the windpipe, or the tracheal carina.
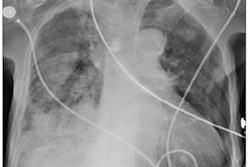
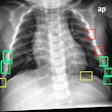
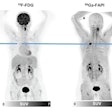
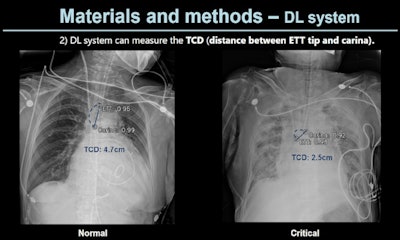 A slide presented by researchers at the ARRS meeting in Hawaii showed measurements used by an AI model for detecting correct endotracheal tube placements in x-rays of intensive care unit (ICU) patients. Image courtesy of Dr. Eui Jin Hwang.
A slide presented by researchers at the ARRS meeting in Hawaii showed measurements used by an AI model for detecting correct endotracheal tube placements in x-rays of intensive care unit (ICU) patients. Image courtesy of Dr. Eui Jin Hwang.Tubes were malpositioned in 76 of the chest x-rays. In a comparison with an experienced thoracic radiologist and one trainee who independently evaluated the placements, the model achieved similar accuracy, the group found.
For deep malpositions of tubes, the model achieved an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.96, and for shallow malpositions of tubes, the model achieved an AUC of 0.97, the researchers reported.
"A DL system showed excellent interrater agreement compared with radiologists in measuring [distance between the tube tip and carina] on chest radiographs," the authors wrote.
With further development and validation, the AI model could facilitate early notification of malpositioned tubes to clinicians for repositioning, they concluded.