A novel x-ray image processing technique called digital variance angiography can improve standard angiography image quality while reducing patient radiation exposure, according to a presentation delivered at the recent RSNA meeting.
German and Hungarian researchers who developed the method compared its performance with standard digital subtraction angiography (DSA) for vascular intervention in patients who have undergone prostatic artery embolization (PAE). They found DVA resulted in significantly higher contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) and could significantly reduce radiation exposure and the amount of iodinated contrast agent required.
"The data in this initial retrospective trial indicate that DVA has significantly higher [contrast-to-noise ratio] and enhanced image quality compared to DSA in PAE procedures," said Dr. Leona Alizadeh of the University of Frankfurt.
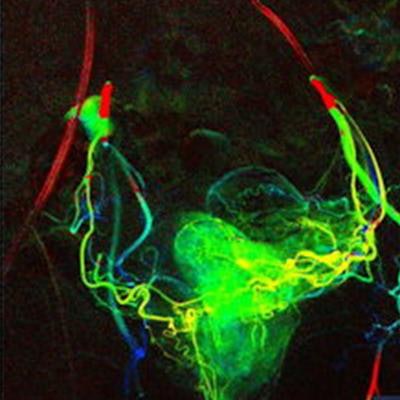
Prostatic artery embolizations require long procedure times and large doses of fluoroscopy contrast agents, Alizadeh said. Digital variance angiography uses the same raw series of x-ray images acquired in digital subtraction angiography, but rather than subtracting the precontrast image from the series, the method applies an algorithm that calculates the variance of each pixel intensity in the series. The technique provides a visual of the motion (called "kinetic" imaging) of contrast agents in blood vessels and can be used in standard-of-care angiography examinations, according to Alizadeh's group. In fact, preliminary studies have shown DVA's potential for lower limb and neuroradiologic interventions with reduced contrast agent and radiation dose.
For their research, the investigators included 37 patients between the ages of 42 and 82 who underwent PAE at Frankfurt University Hospital between May and October of 2020. Altogether, 142 acquisitions were included in the analysis, and DSA and DVA images were generated from the same raw series. Alizadeh and colleagues added color during image processing to enhance visualization of the contrast media according to the color spectrum of visible light and calculated contrast-to-noise ratio values. Three readers evaluated image quality in a randomized blinded survey, using a five-grade-Likert-scale.
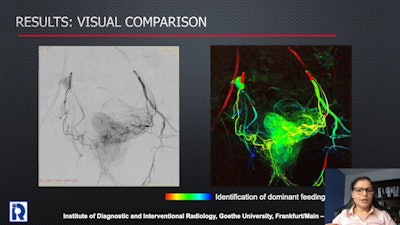 Image courtesy of Dr. Leona Alizadeh.
Image courtesy of Dr. Leona Alizadeh.The group's analysis showed digital variance angiography images provided 4.1 times higher contrast-to-noise ratio than digital subtraction angiography images. The median contrast-to-noise values were 29.5 for DVA and 7.2 for DSA (p < 0.001), and the DVA images received significantly higher Likert scores than DSA images, with median values of 4.33 compared with 3.67 (p < 0.001), respectively.
"This quality reserve of DVA might provide an opportunity for the reduction of radiation exposure and iodinated contrast media in PAE," Alizadeh said.
The group is currently planning to validate the dose management capabilities of DVA in an upcoming clinical trial, she concluded.