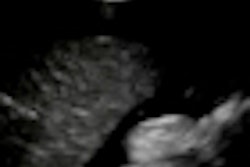
Although less frequently seen than lateral epicondylitis, epitrochleitis (also known as golfer's elbow, medial tennis elbow, or pitcher's elbow) is a common injury in sports that require repetitive valgus stress to the elbow joint. Epitrochleitis treatment varies considerably, however, ranging from conservative methods to surgical intervention, said presenter Dr. Giulio Ferrero of the University of Genoa.
Ferrero and colleagues treat epitrochleitis with an ultrasound-guided percutaneous approach using dry needling and steroid injection; they sought to compare the effectiveness of this combined method to treatment using either only local steroid injection or dry needling.
Patients treated with the ultrasound-guided combined procedure had better outcomes than other groups, the results showed; pain relief was faster and more permanent, Ferrero said. There were also no complications.
"Ultrasound is extremely reliable in the identification and localization of common flexor-pronator tendon lesions, and it offers a precise guidance for the treatment," Ferrero said. "Besides that, this procedure is also easy to perform, quick, and, above all, noninvasive."