Japanese drug developer Eisai has received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for its Leqembi (lecanemab) treatment for individuals with Alzheimer's disease. The drug is the second of a new category of medications for the disease to go through the FDA's accelerated regulatory pathway.
Treatment with Leqembi is indicated in patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia stages of disease, the population in which the treatment was studied in clinical trials. The labeling also states that there are no safety or effectiveness data on initiating treatment at earlier or later stages of the disease, according to the FDA.
"This treatment option is the latest therapy to target and affect the underlying disease process of Alzheimer's, instead of only treating the symptoms of the disease," said Dr. Billy Dunn, director of the Office of Neuroscience in the FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, in a statement.
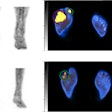
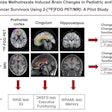
Researchers evaluated Leqembi's efficacy in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, dose-finding study of 856 patients with Alzheimer's disease. Treatment was initiated in patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia stages of the disease. Amyloid PET imaging confirmed the presence of beta-amyloid beta pathology.
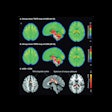
Patients receiving 10 mg/kg of the treatment every two weeks had significant dose- and time-dependent reduction of beta-amyloid plaque brain deposits from baseline to week 79 compared to the placebo arm, which had no reduction of beta-amyloid deposits, according to the results.
"These results support the accelerated approval of Leqembi, which is based on the observed reduction of amyloid beta plaque, a marker of Alzheimer's disease," the FDA said in the statement.
The FDA's accelerated approval pathway is "used for a drug for a serious or life-threatening illness that provides a meaningful therapeutic advantage over existing treatments," according to the FDA.
The prescribing information for Leqembi includes a warning for amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA), which are known to occur with antibodies of this class. ARIA most commonly present as temporary swelling in areas of the brain and are diagnosed on MRI scans.
Eisai led the development and testing of the drug and has again partnered with Biogen for commercialization and marketing. The two companies had previously collaborated on the controversial Alzheimer's drug Aduhelm, the first anti-amyloid plaque monoclonal antibody to reach the market.
Aduhelm was approved by the FDA on June 8, 2021, also via the FDA's accelerated pathway. However, Biogen elected in 2022 to drop further commercial development of the drug following a decision by the U.S. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) to limit Medicare reimbursement for Aduhelm to patients enrolled in clinical trials.
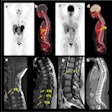
In a related development, a decision is pending on whether the CMS will cover more than a single diagnostic amyloid PET scan per lifetime to help manage these and other patients.