AI models have advanced quickly for research and clinical use, but concerns also have emerged over the possibility of AI deployed in a clinical setting being misused or whether AI models are safe from attack by intentionally manipulated images, according to senior study author Shandong Wu, PhD, of the University of Pittsburgh.
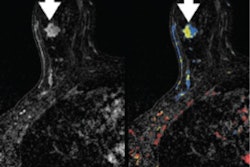
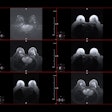
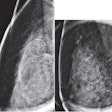
After first building a deep-learning model for breast cancer diagnosis using digital mammogram images, the researchers then used GANs to develop another AI model that can automatically generate fake but real-looking mammograms. Next, they investigated whether the breast cancer diagnosis model could be fooled by the fake images. In addition, they also evaluated whether two experienced radiologists could differentiate the real images from the fake ones.
The researchers found that AI models may be fooled by the fake images that were generated intentionally by automatic computer models to elicit an incorrect diagnosis of breast cancer in certain patients.
"Human radiologists are less interfered by the fake images as they can recognize some of the fake images by visual observation, especially after an education intervention about how the fake images were generated from real images," Wu told AuntMinnie.com. "Our study provides some important insights in this topic and can contribute to educate the community to pay attention to such a key issue."
Find out more about the safety risks to deep-learning algorithms by attending this Tuesday morning presentation.