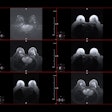
The MRI technique of diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) shows promise for identifying mild cognitive impairment among individuals exposed to environmental toxins, a study published January 21 in Academic Radiology has found.
A research team from Taiyuan, China, found that the technique offered useful information about mild cognitive impairment (MCI) in a cohort of aluminum factory workers.
"[Our study indicated] that the DKI technique could provide valuable information for the diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment," wrote a group led by Wenji Xu, PhD, of Shanxi Medical University.
Mild cognitive impairment is considered to be a transitional stage between normal aging and dementia -- and it can lead to disease such as Alzheimer's, the investigators noted. Interventional measures during a person's MCI phase may slow or stop their progression toward Alzheimer's, however, making "the diagnosis of MCI ... of great significance for delaying onset and progression of dementia," they wrote.
Diffusion kurtosis imaging is an extension of diffusion tensor imaging and can identify small structural changes in the brain before they can be discerned by conventional MRI. Previous studies have shown aluminum buildup in the brain to be associated with mild cognitive impairment, but the efficacy of DKI for assessing it among individuals exposed to environmental toxins is sparse, however.
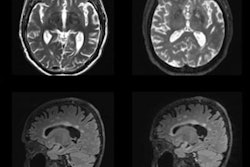
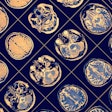
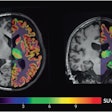
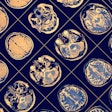
Xu and colleagues conducted a study that included 28 individuals with mild cognitive impairment and 25 healthy controls, all of whom were employed at an aluminum manufacturing facility. All underwent conventional MRI and diffusion kurtosis imaging exams. The researchers investigated the following measures in 10 different areas of the brain (hippocampus, substantia nigra, red nucleus, thalamus, anterior cingulate gyrus, genu and crus of the corpus callosum, and the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes):
- Mean kurtosis (MK)
- Axial kurtosis (Ka)
- Radial kurtosis (Kr)
- Mean diffusivity (MD)
- Fractional anisotropy (FA) parameters
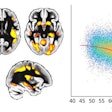
The team then calculated the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve to assess diagnostic efficacy of DKI and evaluated any correlation between the imaging exams and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) tool, which assesses MCI.
Overall, DKI revealed that, compared to healthy controls, patients in the mild cognitive impairment group had lower mean kurtosis, axial kurtosis, radial kurtosis, and fractional anisotropy values, all of which suggest cognitive impairment. Mean kurtosis in the right hippocampus showed the largest AUC for identifying MCI, at 0.92, and it also showed greatest correlation with MoCA scores that suggested MCI.
The team's conclusion? Diffusion kurtosis imaging shows promise for identifying mild cognitive impairment among people exposed to environmental toxins, according to the group.
"The DKI method might be a sensitive imaging biomarker to discriminate MCI from normal controls and could preliminarily assess the severity of cognitive impairment in aluminum-exposed workers," the group wrote. "Mean kurtosis in the right hippocampus appeared to be the best independent predictor."