PET imaging that reveals poor outcomes in patients after a heart attack has won Image of the Year honors at this year's Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) annual meeting.
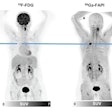
Using a gallium-68-labeled (Ga-68) radiotracer designed to bind to fibroblast cells (Ga-68 FAPI-46), a group from Hannover Medical School in Germany performed fibroblast-activation protein inhibitor (FAPI)-PET imaging in 35 patients several days after they experienced a heart attack. The team found that the FAPI-PET signal in injured heart muscle predicted heart dysfunction in patients more than four months later.
"The early PET signal exhibited a stronger correlation to [left ventricular ejection fraction] at follow-up, suggesting a relationship between the extent of fibroblast activation and worse ventricle remodeling," said nuclear cardiologist Dr. Johanna Diekmann during a presentation before the award announcement.
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the measurement of how much blood is being pumped out of the left ventricle of the heart with each contraction. LVEF is typically reduced in patients after heart attack as the heart muscle undergoes "remodeling" in response to injury. Moreover, fibroblast cells have been shown to be highly active during this molecular process.
In their study, the German researchers showed that the activity of fibroblast cells was strongly correlated with tissue characteristics from cardiac MRI, a standard test for measuring LVEF.
All 35 patients underwent Ga-68 FAPI-46 PET/CT scans, as well as standard perfusion SPECT and cardiac MRI within 11 days after a heart attack. Cardiac FAP volume was determined by PET imaging and the area of injury was defined by SPECT imaging. Cardiac MRI showed functional parameters, such as LVEF. The study authors then studied these data points for potential correlations.
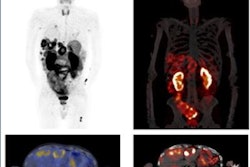
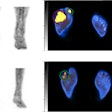
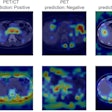
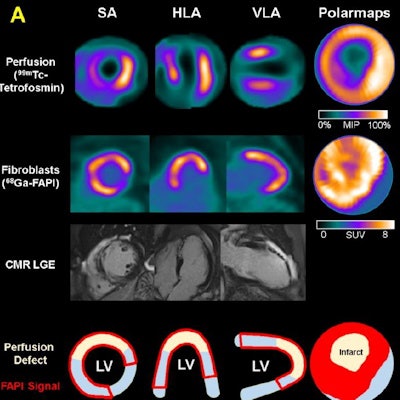
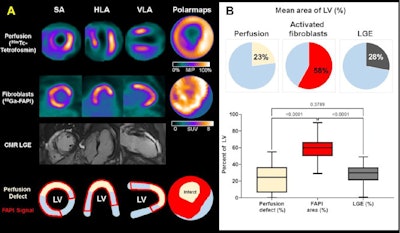 A representative case with acute anterior wall myocardial infarction: Myocardial perfusion images using technetium-99m tetrofosmin at rest (first row), Ga-68 FAPI-46 PET (second row), late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) from cardiac magnetic resonance (third row), and schematic drawings of the left ventricle (fourth row). Area of fibroblast activation exceeds infarct area and LGE signal, the most common type of myocardial FAP-distribution. (Bottom left) Mean areas of perfusion defect, FAPI-signal, and LGE of 35 studied patients. (Bottom right) Global myocardial FAP volume early after acute myocardial infarction inversely correlates with left ventricular ejection fraction (LV-EF) at follow-up in the chronic stage.
A representative case with acute anterior wall myocardial infarction: Myocardial perfusion images using technetium-99m tetrofosmin at rest (first row), Ga-68 FAPI-46 PET (second row), late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) from cardiac magnetic resonance (third row), and schematic drawings of the left ventricle (fourth row). Area of fibroblast activation exceeds infarct area and LGE signal, the most common type of myocardial FAP-distribution. (Bottom left) Mean areas of perfusion defect, FAPI-signal, and LGE of 35 studied patients. (Bottom right) Global myocardial FAP volume early after acute myocardial infarction inversely correlates with left ventricular ejection fraction (LV-EF) at follow-up in the chronic stage.The researchers found fibroblast activity was not only significantly increased in the areas of injury defined by SPECT but also in nearby uninjured areas, and this activity was related to worse outcomes in terms of MRI heart function more than four months later when the patients underwent further tests.
"New antifibrotic therapies such as CAR-T cell therapies could significantly change future therapy of heart failure," Diekmann concluded. "Using FAPI-PET to select patients suitable for therapy would open a new major application for PET in fibrosis and cardiac diseases."
Each year, SNMMI chooses an image that best exemplifies the most promising advances in the field of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging. This year, the SNMMI Image of the Year was chosen from more than 1,000 abstracts submitted to the meeting and voted on by reviewers and the society leadership.
SNMMI Scientific Program chair Dr. Heather Jacene noted in a news release that FAPI is an exciting experimental radiotracer that appears to hold great potential. As shown in this study, Ga-68 FAPI-46 PET/CT clearly indicates profibrotic activity after acute myocardial infarction, she said.
"This could ultimately have a powerful impact on cardiovascular medicine," Jacene said.