Minnies winners, page 3
Scientific Paper of the Year
Winner: Breast cancer screening using tomosynthesis in combination with digital mammography. Friedewald SM et al, Journal of the American Medical Association, June 25, 2014.
 Dr. Sarah Friedewald of Advocate Lutheran General Hospital.
Dr. Sarah Friedewald of Advocate Lutheran General Hospital.The Minnies panel bucked the economics-oriented trend this year by giving the Best Scientific Paper award to a clinical study on digital breast tomosynthesis over a more dollars-and-cents paper authored by a team led by Dr. Richard Duszak (who happened to win the Minnie for Most Influential Radiology Researcher).
The paper's findings aren't earth-shattering to anyone who has followed DBT in the radiology press; the technology increased cancer detection by 29% while reducing recalls by 15%, echoing previous studies on tomosynthesis.
What's significant about the study is that it was published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, one of the most prestigious peer-reviewed journals in the world. In addition, the study included data from a wide variety of practices, indicating that DBT shouldn't just be restricted to high-end academic centers.
Runner-up: Emergency department imaging: Uncompensated services rendered by radiologists nationwide. Duszak R et al, Journal of the American College of Radiology, June 2014.
Best New Radiology Device
Winner: Somatom Force CT scanner, Siemens Healthcare
First launched at the RSNA 2013 meeting, Somatom Force is the third generation of dual-source CT technology from Siemens Healthcare.
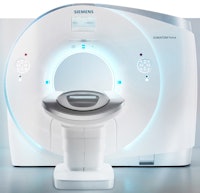 The Somatom Force CT scanner. Image courtesy of Siemens.
The Somatom Force CT scanner. Image courtesy of Siemens.The scanner is based on new Vectron x-ray tubes paired with the latest version of the company's Stellar Infinity detectors, acquiring 384 slices per 0.25-second gantry rotation. Two 120-kW generators deliver up to 2 x 1,300 mA, offering voltages from 70 kV to 150 kV in 10-kV increments.
But horsepower isn't everything, and Somatom Force includes a number of features designed to support scanning with lower contrast and radiation dose. Siemens' Combined Applications to Reduce Exposure (CARE) kV automated exposure control adapts kV to patient size and clinical application. The scanner is also able to routinely scan adults at 70 kV to 90 kV, reducing the amount of contrast that needs to be used, from 90 mL to 110 mL for a thoracic CT scan to about 25 mL to 35 mL.
Meanwhile, Siemens' Turbo Flash mode supports the use of rapid high-pitch scanning, with a scan speed of 737 mm of patient anatomy per second with a 50 cm field-of-view -- enough to cover the entire thorax. This enables use of the company's Flash scanning mode in obese and acute care patients and reduces the number of protocols and amount of preparation time required.
Somatom Force was cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in April 2014.
Runner-up: Revolution CT scanner, GE Healthcare
Best New Radiology Software
Winner: Dose Tracking System, Toshiba America Medical Systems
Developed in collaboration with the University at Buffalo, Toshiba's Dose Tracking System is designed to give interventional physicians a better idea of how much radiation dose patients are receiving during interventional procedures.
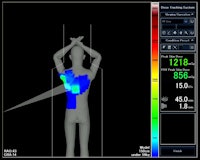 Image courtesy of Toshiba.
Image courtesy of Toshiba.The software debuted in March 2014 at the American College of Cardiology meeting, and it is designed to be used with the company's Infinix-i cardiovascular angiography system.
Dose Tracking System displays real-time and cumulative radiation exposure, with a color-coded indicator on a 3D representation of the patient that demonstrates where radiation is being administered. Interventionalists can then make changes during procedures to distribute the skin dose and minimize the chances of locally concentrated radiation exposure, according to the company.
Toshiba believes the software can be particularly useful during long interventional procedures and in cases where patients have to return to the cath lab within a few months of the initial procedure. It can also be combined with other radiation dose management tools, such as the company's spot fluoroscopy mode, to reduce dose during cardiac interventions.
Runner-up: Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) planning software, Philips Healthcare
Best New Radiology Vendor
Winner: Analytical Informatics
What does the winner of the Best New Radiology Vendor award in the 2014 edition of the Minnies have to do with this year's theme of economics? Plenty -- Analytical Informatics develops software that gives radiology facilities a platform for measuring economic metrics such as modality utilization and staff efficiency.
 Image courtesy of Analytical Informatics.
Image courtesy of Analytical Informatics.Analytical Informatics has its roots in work done by the radiology informatics team at the University of Maryland, according to co-founder, president, and CEO Chris Meenan, who is still on the faculty at the institution. The team developed software productivity tools for internal use at the university, but soon realized that the software could have broader applications in the external world.
Analytical Informatics was formed in 2011 to be a vehicle for achieving that vision. The company's AI Bridge platform is designed to pull data from different locations around a healthcare enterprise, such as an electronic medical record (EMR), and "normalize" the data for viewing by department administrators.
The firm describes AI Bridge as an ecosystem, with applications operating within the environment. So, it has built more than 30 applications to address various productivity issues, such as patient wait times, workflow optimization, and peer review.
But AI Bridge serves as more than just a vehicle for Analytical Informatics' own software. Sites that purchase AI Bridge also get -- at no extra charge -- a software development kit (SDK) that enables them to build their own applications
"There are a lot of great ideas coming out of academic centers, but it's hard if you build it one place to make it work at another place," Meenan told AuntMinnie.com. "We thought, if we build this tool, other sites could make their own tools to work across other sites."
Meenan envisions the growth of a community of developers creating software based on AI Bridge, a trend that is already happening as academic centers write applications using the platform, he said. Ultimately, an application marketplace could rise up to make it easy for facilities to find the productivity tools they need.
At the upcoming RSNA 2014 meeting, Analytical Informatics plans to launch several new tools, including a clinical quality dashboard that lets administrators and hospital executives build their own dashboards and data viewing tools for different efficiency metrics.
Runner-up: Brain Bioscience
Best Radiology Mobile App
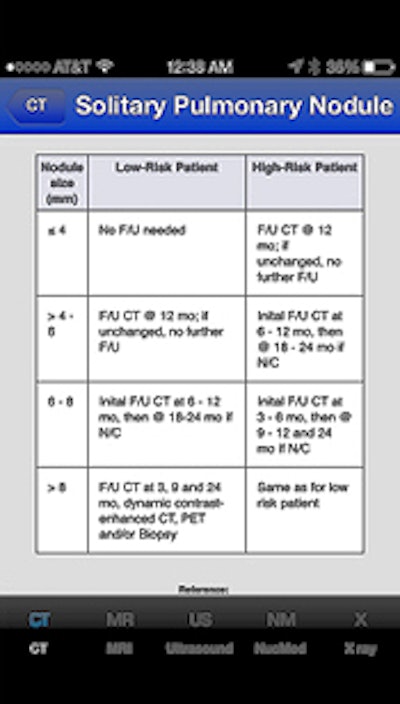
Winner: Radiology Toolbox Pro (iOS), Softcode Systems
This year's winner in the Best Radiology Mobile App category is Radiology Toolbox Pro, developed by radiologist Dr. Eric Baumel, who co-founded Softcode Systems to create educational and decision-support tools for healthcare.
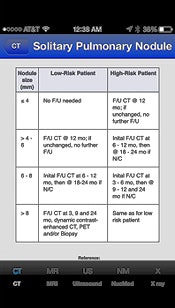 Radiology Toolbox Pro guideline chart as seen on an iPhone. Image courtesy of Dr. Eric Baumel.
Radiology Toolbox Pro guideline chart as seen on an iPhone. Image courtesy of Dr. Eric Baumel.Baumel developed Radiology Toolbox Pro because he found that he was looking up the same facts over and over when reading cases. He figured that having such resources in the palm of his hand via a mobile app would be more efficient than consulting multiple charts, diagrams, and notes taped on the walls.
Remarkably, Baumel developed the app himself, teaching himself coding languages to do so. He also created the medical illustrations that appear in the app.
Radiology Toolbox Pro includes a number of key resources, such as calculators for glomerular filtration rate and adrenal adenoma washout, as well as a cervical lymph node level diagram, solitary pulmonary nodule chart, and contrast premedication information.
The app comes in Lite and Pro versions -- the Lite version has been downloaded nearly 70,000 times worldwide, while the Pro version has been downloaded by more than 4,500 users. Softcode Systems is planning an update for the first quarter of 2015 that will add a dozen new tools, Baumel said.
Runner-up: CTisus iLecture series (iOS), Dr. Elliot Fishman
Best Radiology Image
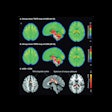
Winner: PET of patient with grade III glioma using iodine-124 (I-124) CLR1404 radiopharmaceutical
This year's Best Radiology Image award went to researchers from the University of Wisconsin for their image series demonstrating a new PET radiopharmaceutical for brain imaging. They believe the agent could more effective than nuclear medicine's workhorse tracer, FDG.
The team led by Dr. Lance Hall, an assistant professor of radiology at the university's UW Health system, has been investigating iodine-124 (I-124) CLR1404, which is being developed for both diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
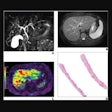
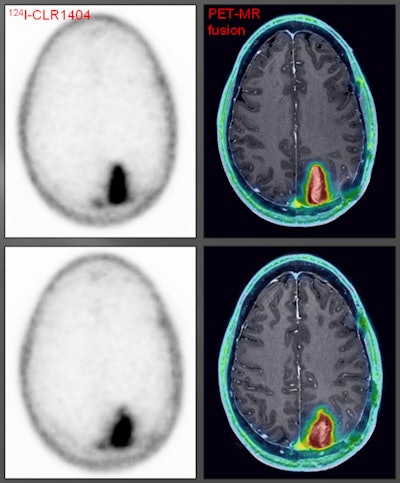 A patient with a grade III glioma was scanned using an iodine-124 (I-124) CLR1404 radiopharmaceutical. PET with CLR1404 detected the cancer, and fused PET/MRI delineated the tumor. Images courtesy of Dr. Lance Hall and the University of Wisconsin's UW Health.
A patient with a grade III glioma was scanned using an iodine-124 (I-124) CLR1404 radiopharmaceutical. PET with CLR1404 detected the cancer, and fused PET/MRI delineated the tumor. Images courtesy of Dr. Lance Hall and the University of Wisconsin's UW Health.CLR1404 is designed to enter cells through membrane lipid rafts, which are overexpressed in cancer cells and serve as a platform for cell proliferation. The agent is taken up by cancer stem cells, which are difficult to eradicate and can lead to disease recurrence and progression if they are not eliminated.
Studies in preclinical models have demonstrated that CLR1404 is more cancer-specific and targets cancers rather than inflammation or false positives that might be found on FDG-PET scans. In the study that resulted in the award-winning images, 16 patients with primary or metastatic brain tumors were injected with the radiopharmaceutical.
CLR1404 successfully imaged tumors with high tumor-to-background uptake and uncovered larger tumor volumes than contrast-enhanced MRI, the researchers found. There was no significant uptake of CLR1404 in normal areas of the brain and no uptake in regions that were treated for cancer and were presumably tumor-free.
Runner-up: CT lung image with computer-aided software