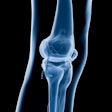
Research from South Korea suggests that 3D isotropic proton density-weighted MR imaging with multiplanar reconstruction is comparable to 2D MR imaging in diagnostic evaluation of the knee.
The study, led by Dr. Sooho Bae, was designed to compare the accuracy of the two MRI technologies in diagnosing knee problems on a 3-tesla MR unit.
Over a four-month period, researchers from the Samsung Medical Center at Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine in Seoul enrolled 20 men and 13 women (mean age, 45 years) for the study.
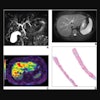
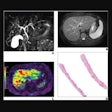
2D MRI scans included proton density-weighted axial, coronal, and sagittal planes, along with T2-weighted sagittal plane. 3D isotropic proton density-weighted MR sequence was obtained using turbo spin-echo with a voxel size of 0.5 x 0.5 x 0.5 mm, with scan times of approximately seven minutes.
Two independent musculoskeletal radiologists retrospectively evaluated the images for anterior cruciate ligament, posterior cruciate ligament, medial meniscal, and lateral meniscal tears, as well as cartilage lesions, using the multiplanar reconstruction technique with the 3D isotropic proton density-weighted MR sequence.
Their review revealed 13 anterior cruciate ligament tears, three posterior cruciate ligament tears, 13 medial meniscal tears, six lateral meniscal tears, and 45 cartilage lesions.
In a detailed comparison of sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy, comparative results from the two radiologists showed no significant differences. In all five categories of knee conditions, 2D MR imaging and 3D isotropic MR imaging were within a few percentage points of agreement. In several areas, sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were 100%.
Radiologists' reviews of 2D MR and 3D isotropic MR images
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: Dr. Sooho Bae | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Based on these results, the "diagnostic performance of knee 3D isotropic proton density-weighted MR imaging using multiplanar reconstruction is comparable to that of 2D MR imaging," the researchers wrote in a study abstract.
As for the patients, subsequent treatment resulted in 23 arthroscopic surgeries and nine total knee replacements.
Study results were presented at the annual 2008 RSNA meeting in Chicago.
By Wayne Forrest
AuntMinnie.com staff writer
February 18, 2009
Related Reading
Isotropic 3T MRI aids in diagnosing labrum, rotator cuff tears, December 29, 2008
MR arthrography outdoes 3-tesla MR on tendon tears, December 12, 2008
MR arthrography study finds 'optimal injection site,' October 24, 2008
Making the most of MRI to assess the rotator cuff pre- and postinjury, November 9, 2007
MRI keeps pace with rapidly evolving musculoskeletal systems of young athletes, May 20, 2007
Copyright © 2009 AuntMinnie.com