Mycobacterium kansasii:
Clinical:
Pulmonary infection with M. kansasii occurs in certain immune competent patients- especially those with underlying COPD, bronchiectasis, and other underlying pulmonary diseases. In these patients, the infection is very similar to that of post-primary TB with apical cavitary disease. The infection is also noted in immune compromised patients, especially HIV patients with CD4 counts below 100/mm3. Unlike MAC infection, however, disseminated disease is not common (12%). If untreated, the infection can be fatal in the immune compromised. Treatment is with rifampin and a majority of patients will demonstrate clinical and radiographic improvement following the initiation of therapy.
X-ray:
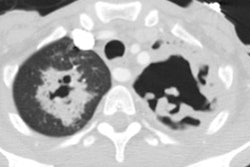
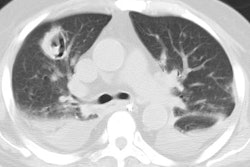
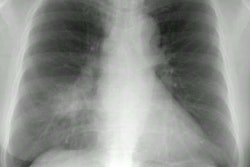
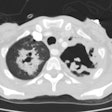
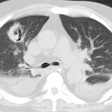
Immune compromised: The radiographic findings have been described in only a small number of patients (#16). The most common finding is airspace disease (75%), which is less frequently cavitary (19%). The infiltrate is unilateral and unifocal in the majority of cases (75%). The infiltrate occurs with roughly equal frequency in the upper, mid, and lower lung zones. Adenopathy is not uncommon (25%), and may be the only finding indicative of infection in immune compromised patients (adenoapthy is rare in immune competent patients). Pleural effusion can be seen in up to 12% of cases. The film can be normal in up to 6% of cases.
REFERENCES: