Minnies finalists, page 3
Scientific Paper of the Year
Breast cancer screening using tomosynthesis and digital mammography in dense and nondense breasts. Rafferty EA et al, Journal of the American Medical Association, April 26, 2016. To learn more about this paper, click here.

The clinical evidence backing digital breast tomosynthesis has been building, but the technology's momentum got a big push forward by the publication of this paper in JAMA from a group led by Dr. Elizabeth Rafferty of L&M Radiology in West Acton, MA.
In the paper, Rafferty and colleagues found that using tomosynthesis with digital mammography improved cancer detection rates by 48% in women with dense breast tissue, while also reducing recall rates.
The findings are particularly significant due to conventional mammography's problems with detecting cancer in women with dense breast tissue. Should the findings be validated with other studies, tomosynthesis could become a versatile breast screening tool that may not require the use of supplemental modalities for women with dense breast tissue.
Cancer risks in U.S. radiologic technologists working with fluoroscopically guided interventional procedures, 1994-2008. Rajaraman P et al, American Journal of Roentgenology, May 2016. To learn more about this paper, click here.

Most of the concerns about radiation dose in medical imaging have focused on patient exposure. But researchers are beginning to realize that another group -- radiologic technologists (RTs) -- are also at risk.
In this study, researchers from the U.S. National Cancer Institute wanted to examine cancer incidence rates for RTs who perform fluoroscopically guided interventional procedures and compare them with rates for technologists who perform diagnostic exams, which don't require as much radiation. The survey covered two time periods, 1983 to 1989 and 1994 to 1998, with follow-up data on cancer incidence and mortality acquired after that.
The group found that interventional RTs had twice the risk of brain cancer mortality, as well as slightly higher incidences of melanoma and breast cancer, but not mortality. There was no elevated risk for a number of other cancer types.
What do the numbers mean? More research is needed, the authors wrote, but the findings highlight the need to continue keeping radiation dose as low as possible -- for both patients and providers.
Best New Radiology Device
Affirm prone breast biopsy system, Hologic
 Affirm prone breast biopsy system
Affirm prone breast biopsy systemCandidates related to digital breast tomosynthesis are finalists in several Minnies categories this year, and the race for Best New Radiology Device is no exception.
The Affirm dedicated prone biopsy system from Hologic is designed to work with both conventional 2D and 3D tomosynthesis mammography, such as the company's Genius 3D mammography unit, and complements an upright biopsy unit already in the company's portfolio. Prone biopsy offers a number of advantages and is likely to further enhance the utility of tomosynthesis in everyday breast imaging practice.
Hologic claims that the system has a larger field-of-view than other prone biopsy devices, and it gives 360° access to lesions thanks to an integrated C-arm. The Affirm prone biopsy unit was launched in Europe in March 2016 and received U.S. Food and Drug Administration clearance in April.
OnSight 3D extremity imaging CT scanner, Carestream Health
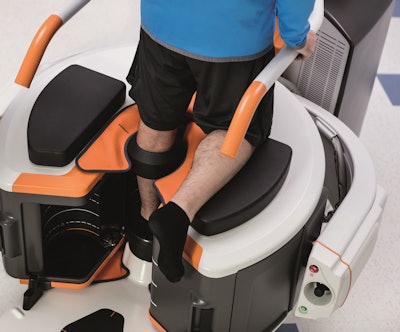 OnSight 3D extremity imaging CT scanner
OnSight 3D extremity imaging CT scannerOnSight 3D is unique not only for its product niche -- a small CT scanner designed for extremity studies -- but also because of who's selling it: Carestream Health, a firm known more for digital x-ray and imaging informatics products.
OnSight 3D is designed for weight-bearing scans that are typically performed for orthopedic applications. It's targeted at orthopedic practices as well as hospitals that might want a second CT unit to free up a whole-body system for other exams. The system also comes with 3D software from Carestream designed to give orthopedic specialists more information on pathology than what might be possible with 2D imaging.
OnSight 3D represents part of a push by Carestream to find new markets outside of its traditional focus on digital x-ray and imaging informatics. The company in 2014 introduced its Touch ultrasound scanner, and OnSight now gives the firm offerings in the three largest markets in medical imaging: x-ray, CT, and ultrasound.
Best New Radiology Software
Note: Due to a tie for second place, there are three finalists in this category.
4D Flow, Arterys
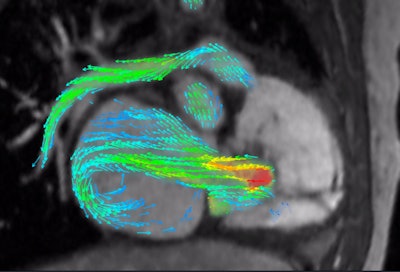 4D Flow depicts severe regurgitation on right-ventricular three-chamber view. Image courtesy of Arterys.
4D Flow depicts severe regurgitation on right-ventricular three-chamber view. Image courtesy of Arterys.Developed by deep-learning technology developer Arterys, 4D Flow uses cloud-based image processing technology to provide visualization and quantification of blood flow on cardiac MRI studies.
With 4D Flow, cardiac MRI exam times can be sharply reduced to just 10 minutes, according to the company. After the software is connected to a standard MRI scanner, a simple MRI exam of the chest can be uploaded to the firm's cloud server, Arterys said. Deep learning and artificial intelligence techniques are then applied to provide the clinician with quantitative clinical analysis.
Arterys first introduced 4D Flow in collaboration with GE Healthcare at RSNA 2015, and it is currently teaming up with GE on a prelaunch pilot introduction at 15 to 20 sites around the world, according to the firm. 4D Flow will initially be incorporated into GE's ViosWorks cardiac software package.
In addition to being selected as a finalist for Best New Radiology Software, Arterys is also a finalist this year for Best New Radiology Vendor (see below).
ICE-T inpatient cost evaluation tool, Harvey L. Neiman Health Policy Institute

Our second finalist for Best New Radiology Software is designed to help radiology practices and hospitals make good decisions about whether to develop or participate in bundled payments for radiology services.
Available as a free resource on the Health Policy Institute's website, the Inpatient Cost Evaluation Tool (ICE-T) allows internal benchmarks to be compared with national average benchmark price points. Focusing on factors related to value, variance, and volume, ICE-T can show radiology providers where their costs and risks are, according to the institute.
The institute aggregated many years of national inpatient Medicare claims data to provide information on total hospital reimbursement, total imaging reimbursement, and imaging's share of reimbursement across inpatient diagnosis-related groups (DRGs). ICE-T users can compare up to four inpatient DRG components and also find and rank DRGs by frequency.
PACS Redefined, Lexmark International
 Image courtesy of Lexmark.
Image courtesy of Lexmark.Rounding out the category, Lexmark International's PACS Redefined offers a modular suite of software and services to support enterprise imaging.
PACS Redefined is designed to free healthcare organizations from being tied to a particular vendor, Lexmark said. The software and services suite is also intended to streamline image sharing and access throughout the enterprise and can image-enable an electronic health record (EHR) or other core clinical system, according to the vendor.
Components include the company's Acuo vendor-neutral archive (VNA), NilRead Interpretation viewer for diagnostic image interpretation, NilRead Enterprise viewer for nondiagnostic image viewing from an EHR or VNA, and Clario worklist management software.
Best New Radiology Vendor
4Dx
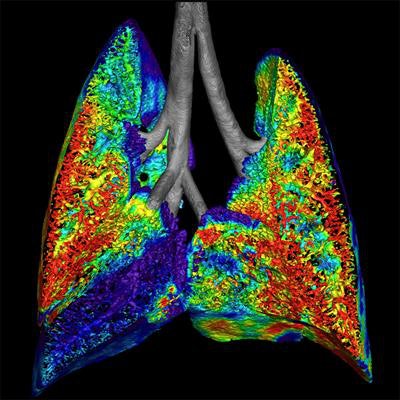 Preclinical image of cystic fibrosis shows ventilation using a fluoroscopy acquisition. Image courtesy of Dr. Andreas Fouras and Dr. Rajeev Samarage.
Preclinical image of cystic fibrosis shows ventilation using a fluoroscopy acquisition. Image courtesy of Dr. Andreas Fouras and Dr. Rajeev Samarage.Australian start-up 4Dx has garnered attention for its technology that combines fluoroscopy and advanced visualization to generate high-resolution images of motion and airflow in lung tissues.
4Dx executives hope their algorithm will enable researchers to view and measure abnormal function in lung regions at the earliest clinical stages of disease. If applied to chronic lung conditions, the technique can quickly assess the patient's condition both qualitatively and quantitatively, and potentially replace several pieces of diagnostic information from difference sources that are currently needed to find out what's going on in the lungs, according to the company.
Testing on human subjects is now underway, 4Dx said. The company plans to file its first 510(k) application with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in early 2017, involving use of the technique in patients who need frequent follow-up for chronic lung diseases such as cystic fibrosis, those who have received a lung transplant, or patients undergoing radiotherapy who may experience lung toxicity.
Arterys
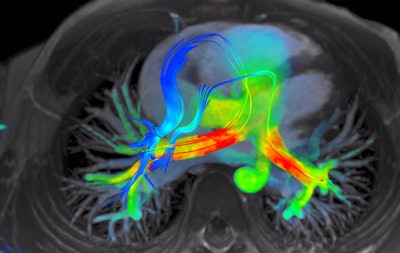 4D Flow software for cardiac MRI shows streamlines of shunted pulmonary venous flow back out to each pulmonary artery. Image courtesy of Arterys.
4D Flow software for cardiac MRI shows streamlines of shunted pulmonary venous flow back out to each pulmonary artery. Image courtesy of Arterys.Cloud-based deep-learning technology developer Arterys is also making waves with its 4D Flow algorithm for cardiac MR image visualization and quantification. In fact, 4D Flow is also a finalist for Best New Radiology Software (see above).
The company is preparing for the global launch of 4D Flow in partnership with GE Healthcare, according to the company. The two firms inked a partnership late last year and showcased the Arterys software as part of GE's ViosWorks cardiac software package at RSNA 2015.
In addition to adding more cardiac MR functionality to 4D Flow, Arterys plans to develop other applications on its platform, including investigating opportunities in oncology and neurology. Other technology currently being developed for radiology includes longitudinal tracking of anatomy with the ability to detect changes, multiparametric image processing, and -- in a long-term project -- building predictive analytics based on phenotypes of different conditions, Arterys said.
Best Radiology Mobile App
CTisus Critical Diagnostic Measurements in CT (iOS), Dr. Elliot Fishman
 CTisus Critical Diagnostic Measurements in CT
CTisus Critical Diagnostic Measurements in CTIf you're going to interpret CT exams, you need to know both normal anatomy and the alterations in size and attenuation that are indicative of pathology. That's the concept behind CTisus Critical Diagnostic Measurements in CT, an educational iPad app and finalist for Best Radiology Mobile App.
Not only does the app provide normal measurements of a range of anatomic structures, it also includes critical size and Hounsfield unit thresholds for distinguishing benign lesions from potentially malignant or life-threatening pathology, according to developer Dr. Elliot Fishman of Johns Hopkins Hospital. To help users build their knowledge base, the app also facilitates access to the literature used to derive this information.
Notably, this is the third finalist nomination in a row in the Best Radiology Mobile App category for Fishman's CTisus family of educational CT mobile apps.
Kanal's MR Safety Implant Risk Assessment (iOS), Dr. Emanuel Kanal
 Kanal's MR Safety Implant Risk Assessment methodically guides users through an assessment of all MR safety-related conditions. Image courtesy of Dr. Emanuel Kanal.
Kanal's MR Safety Implant Risk Assessment methodically guides users through an assessment of all MR safety-related conditions. Image courtesy of Dr. Emanuel Kanal.Even though MRI has been around for over three decades, adverse events still happen all too often. The vast majority of these events are completely preventable, however, according to longtime MRI safety advocate Dr. Emanuel Kanal of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center.
That said, it may not be obvious whether a patient with a metallic device or foreign body can safely undergo a requested MRI examination. To help with this challenging task, he developed Kanal's MR Safety Implant Risk Assessment, an iOS app.
The app is designed to help users understand the underlying potential safety concerns of exposing patients to the MR imaging environment, and it also guides them through the process of assessing and quantifying the relative risks of permitting a patient to receive a specific MR exam. Kanal created the app primarily as an adjunct for attendees of his MR safety training courses.