CHICAGO - Multimodality vendor GE Healthcare is demonstrating a range of new technologies in its RSNA booth, including a new high-definition CT platform, an MRI scanner for dedicated breast imaging, and technology for freezing motion in PET/CT studies.
CT
The major highlight in the CT area of GE's booth is a package of technologies that GE is referring to as its high-definition CT (HDCT) platform. The HDCT platform involves the use of new detector materials, a redesigned imaging chain, and new x-ray tube technology to produce images with higher spatial resolution.
 |
| GE's high-definition CT (HDCT) x-ray tube. |
On the imaging chain side, GE engineers are extending the capabilities of the vendor's Volara digital acquisition system to more than double its sampling speed over other scanners on the market, while also maintaining low-signal performance for dose efficiency.
HDCT's x-ray tube also represents a technology advance in that it uses an electrostatically controlled photospot that enables the tube to rapidly switch kV energies in less than 1 msec. This enables the system to perform dual-energy imaging simultaneously without having to resort to a dual-source design.
The primary benefit of HDCT technology is much improved image quality, according to GE. The company is demonstrating images collected with the system that clearly demonstrate 200-micron struts in stents implanted in patients. Another benefit is lower radiation dose, according to GE -- because the system collects and reconstructs data more efficiently, less power is required to produce high-quality images. GE believes that HDCT technology will result in 50% lower dose throughout the body.
HDCT is based on 64-slice CT architecture. The technology is being shown as a work-in-progress, as it has not yet received clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
In addition to HDCT, GE is touting new clinical results validating the ability of its SnapShot Pulse prospectively gated cardiac CT technique to reduce radiation dose. Clinical users are finding that SnapShot Pulse reduces radiation dose as much as 83% for cardiac studies. Another GE technique, VolumeShuttle, collects up to 8 cm of anatomical coverage with 24% less radiation dose compared to a conventional 4-cm cine profusion protocol.
On the clinical side, GE is discussing the results of a clinical trial evaluating the diagnostic accuracy of 64-slice coronary CT angiography to detect obstructive coronary stenosis compared to conventional coronary angiography.
MRI
GE is demonstrating a pair of new scanners at the meeting, each based on enhancements to the company's Signa HDx platform.
Signa Vibrant is a 1.5-tesla scanner dedicated exclusively to breast MR applications. The scanner is based around the company's Vibrant breast imaging technique, and includes a special patient table developed by Sentinelle Medical of Toronto for breast imaging applications.
The Sentinelle table supports eight- or 16-channel coils, and is designed to enable breast biopsy procedures to be performed easily in the MR suite. The table can be detached for the MR scanner, and sites that own two Sentinelle tables can prepare a patient on one table while the next patient is being scanned, improving throughput.
In addition to the Vibrant technique, the new scanner supports GE's Brease breast spectroscopy protocol and the CADStream breast MR CAD application from Confirma of Bellevue, WA.
GE's other new MR offering is Signa HDxt, which is built around new applications included in a new software release and available in 1.5- and 3-tesla configurations. The applications include Ideal, an application for fat suppression that produces four images from one acquisition. Ideal provides water-only images that can include uniform fat suppression, multiple contrasts in one acquisition, and minimal artifacts, according to the company.
The other HDxt application, Cube, can replace standard 2D acquisitions acquired in multiple planes with a single accelerated 3D volume scan. Users can view high-definition 3D data from one acquisition in any plane, including axial, sagittal, coronal, or oblique, with no gaps or resolution loss, according to the company. Cube is enabled by GE's Arc parallel acquisition technique.
Finally, GE announces a new set of software releases in its ContinuumPak for installed Signa scanners. The new package includes postprocessing and reporting tools, parallel imaging acceleration, and 3D dual-echo techniques.
Molecular imaging
In molecular imaging, GE is exhibiting its MotionFree imaging technology and new Vue Point High Definition (HD) applications to help detect lesions as small as 3 mm and enhance image processing.
 |
| GE is featuring its PET/CT MotionFree imaging technology in its RSNA booth. |
Through motion-free imaging, the technology could enable physicians to see disease earlier, localize and personalize treatment, and carefully monitor treatment.
GE's new version of the Discovery Dimension PET/CT scanner will include motion-free imaging. The system's features include motion-correction techniques to enhance clinical results and minimize blur caused by motion. For patients, the result can be enhanced radiation treatment planning through more accurate tumor delineation for a more precise treatment plan.
GE's Vue Point HD PET image processing application also is designed to improve small lesion detectability. Available on Discovery Dimension with new installations or by field upgrades for installed Discovery ST systems, the upgrade enables clinicians to perform advanced PET image generation for both qualitative and quantitative accuracy.
Vue Point HD incorporates proprietary advanced image reconstruction algorithms, including volume scatter correction and a patented image projection technique. It is applicable to both 2D and 3D PET acquisition modes, as well as static, dynamic, and motion imaging.
PACS/healthcare informatics
In image and information management, GE is unveiling a suite of Centricity products for hospitals and outpatient imaging centers. The product line builds on existing Centricity technology and clinical capabilities, and adds the Web-based accessibility of IntegradWeb (IW) products GE acquired from its recent purchase of PACS firm Dynamic Imaging.
Centricity Radiology-IW for hospitals will feature Web-based portability, image reporting, and scalable business processes.
Centricity RIS/PACS-IW (formerly IntegradWeb RIS/PACS) targets outpatient imaging centers and features a Web-based, single-desktop technology to enhance efficiency and productivity for radiologists and referring physicians.
GE is also unveiling Centricity OutReach-IW for distribution of imaging results. Centricity OutReach-IW brings Web-based distribution to current Centricity customers, offering referring physicians unlimited access to images and reports within a Web browser.
Products within the Centricity IW line are scheduled for availability in the first half of 2008.
Ultrasound
Increased productivity is the goal for upgrades in GE's Logiq ultrasound product line on display at RSNA 2007, as the company's ultrasound systems target several radiology care areas, such as pediatric radiology, vascular applications, and breast imaging.
Rather than storing ultrasound images as video pixels, Logiq's data is stored as digitized ultrasound waveforms for enhanced high ultrasound fidelity. Data can be captured in 3D in near real-time, making ultrasound imaging "more CT-like," according to the company. Clinicians can view, reprocess, reslice, and review images after an ultrasound scan.
GE's Tomographic Ultrasound Imaging (TUI) technique also gives clinicians access to parallel slices through captured data, similar to MR and CT.
Many clinicians are using 3D ultrasound in Volume Imaging Protocol (VIP). Patients and clinicians can be spared the time and expense of additional scans with advances in image acquisition and processing. VIP also allows for an ultrasound scan on babies in a neonatal intensive care unit in less than a minute to acquire the same data that would be required in a 10-minute traditional study. The reduction in scan time is also expected to help minimize repetitive motion injuries with sonographers and other equipment operators.
Mammography
In the mammography section of its booth, GE is highlighting its ongoing work to develop a digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) mammography unit, which uses a motorized tube head to collect multiple slice-based views that can be reconstructed into volume images. DBT proponents believe the technology can help clinicians see around anatomical structures that might be obscuring pathology.
GE has investigational DBT units installed at seven sites around the world that have collected 1,500 to 2,000 patient studies in preparation for a premarket approval (PMA) submission to the FDA. Given the nature of the PMA process, it could be up to two years before a DBT-based mammography system is available commercially.
Other mammography highlights include Senographe Mobile Essential, a full-field digital mammography system designed for mobile use, and the company's recent alliance with iCAD of Nashua, NH, to develop customized computer-aided detection (CAD) software for GE's Senographe and Seno Advantage systems.
In bone mineral testing, GE is announcing Mobile Prodigy, the first offering of its fan-beam dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry technology for mobile use.
X-ray
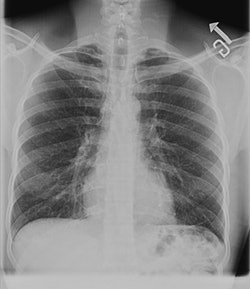 |
| A digital chest image taken with GE's VolumeRad technology. |
VolumeRad collects 40 to 60 low-dose tomographic slices in a five-second sweep of the system's overhead tube crane. The slices can then be reconstructed into volume images. GE believes the technique can be useful for applications such as ruling out pathology in patients who otherwise might be sent on for more expensive modalities like CT and MRI.
The company has been shipping VolumeRad for the past three months, and has 100 of the systems installed.
By Brian Casey and Wayne Forrest
AuntMinnie.com staff writers
November 26, 2007
Related Reading
GE, iCAD partner, November 21, 2007
GE debuts Centricity OneView, November 21, 2007
GE names Blackwood to VP post, November 21, 2007
GE to build new digital detector plant, November 16, 2007
GE adds to cardiac offerings at AHA show, November 8, 2007
Copyright © 2007 AuntMinnie.com